Nodes are small functional blocks that each perform a specific task — like creating points, generating curves, doing math, or modifying geometry. Every node takes inputs, processes them, and gives outputs.
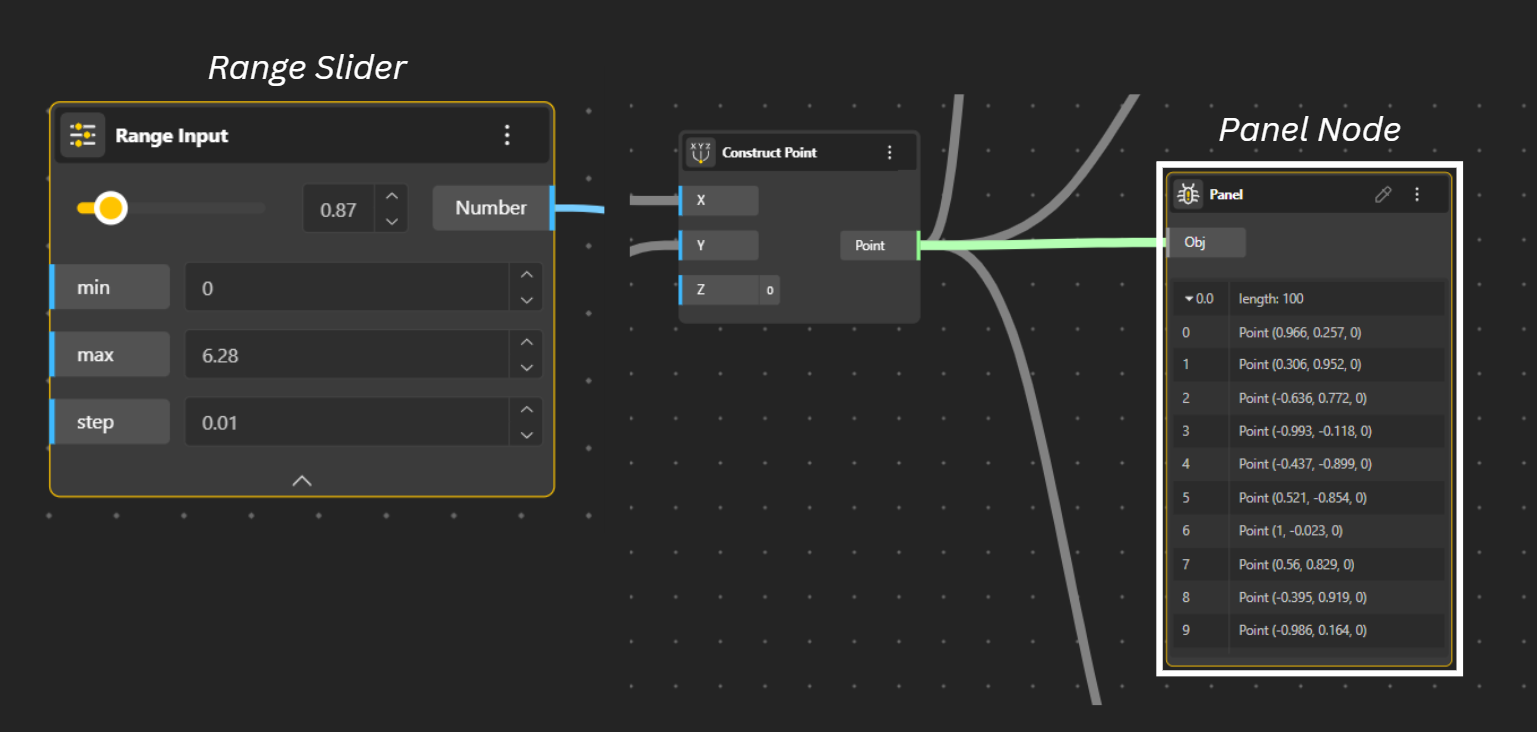
To Perform operations - Each node has a specific function, like a mathematical operation or a geometry-generating command. For example, a "Construct Point" node uses input data (X, Y, Z coordinates) to create a point.
When an input value changes (for example, by moving a number slider), the node re-executes its logic, and the entire chain of nodes updates automatically to reflect the new result.
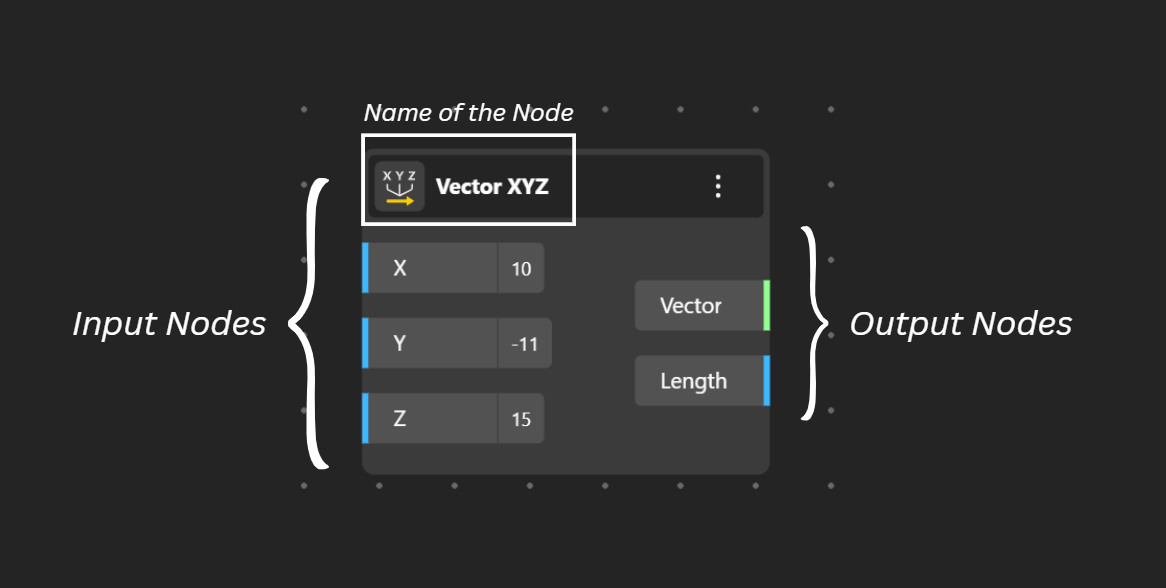
The node is Divided into three Parts:
INPUT (left) / STORE or PROCESS DATA (center) / OUTPUT (right)
Receive inputs and produce outputs: Nodes have inputs on the left and outputs on the right, which are connected to other nodes. The output of one node becomes the input for the next, creating a chain of operations.
Store and process data: There are two main types of nodes: parameters for storing data (like a number slider) and arithmetic units for processing that data (like a calculation or a geometric command).
Add nodes: You can add nodes by dragging them from the toolbar, double-clicking the canvas and typing the component's name, or dragging them from a panel.
Connect nodes: To create a workflow, connect the output of one node to the input of another by clicking and dragging a wire between the two. Grasshopper typically works from left to right.
Adjust parameters: Use other nodes, like a "Number Slider," to control the inputs of a component to dynamically change the design.
Inspect the data: Use "Panel" nodes to display the data flowing through the network, which is helpful for understanding and debugging.