The Math menu contains nodes that perform mathematical operations on numbers, lists, vectors, and parameters inside your graph. These nodes help you calculate values, transform inputs, and build logic for geometry or data.
Below is the first category:
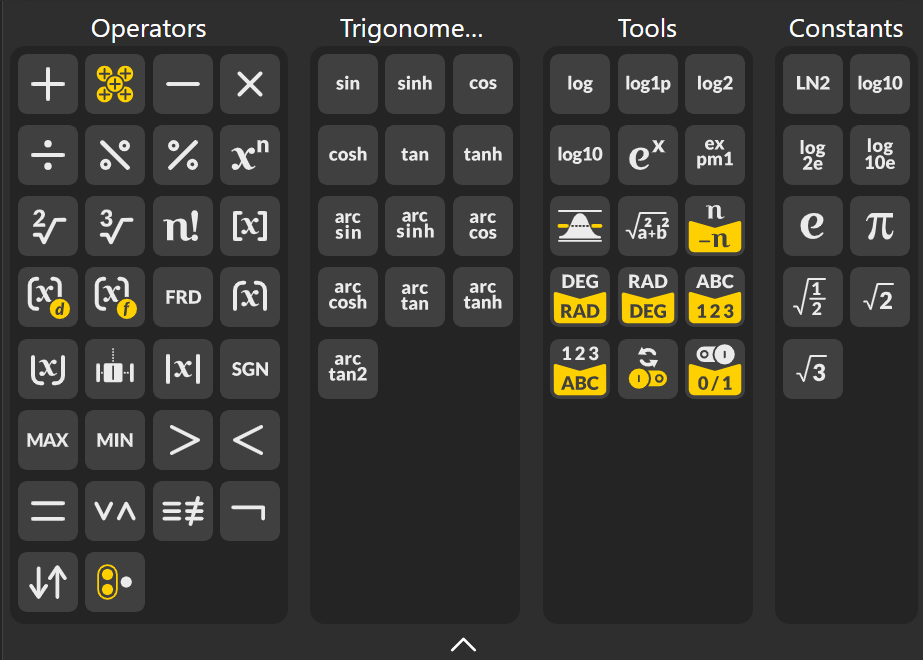
Nodes that handle fundamental mathematical functions such as:
Addition: Adds two or more numbers.
Mass Addition: Adds an entire list of numbers and outputs a single summed value.
Subtraction: Subtracts one value from another.
Multiplication: Multiplies two or more numbers.
Division: Divides a value by another value.
Integer Division: Division that returns only the integer part (no decimals).
Modulus: Returns the remainder after integer division.
Useful for cycles, patterns, indexing.
Power: Raises a number to a chosen exponent (x^n).
Square Root: Returns √x.
Cube Root: Returns ³√x.
Factorial: Multiplies all positive integers up to n (n!). Common in combinations, permutations, series.
Round [x]: Rounds to the nearest whole number.
Round to Decimal Place: Rounds a value to a specific number of decimals.
Round to Factor: Rounds a number to the nearest multiple of a chosen factor.
Fround Rounds using floating-point rounding (IEEE-754 style).
Ceil: Rounds up to the next whole number.
Floor: Rounds down to the previous whole number.
Trunc: Removes the decimal part (cuts off digits without rounding).
Absolute: Returns the positive magnitude of any number.
Sign: Returns −1, 0, or +1 depending on the sign of the value.
Max: Outputs the largest value in the input set.
Min: Outputs the smallest value in the input set.
Larger: Compares two numbers and outputs the larger one.
Smaller: Compares two numbers and outputs the smaller one.
Equality: Checks whether two values are exactly equal.
Gate AND / OR
AND: True only if all inputs are true
OR: True if any input is true
Gate XOR / XNOR
XOR: True if inputs are different
XNOR: True if inputs are the same
Gate NOT: Inverts the input (true → false, false → true).
Gate NAND / NOR
NAND: NOT(AND)
NOR: NOT(OR)
Gate Majority: Outputs true if the majority of inputs are true.
Here are the Trigonometric tools, which let you calculate standard, inverse, and hyperbolic sine, cosine, tangent, and related functions inside your graph.
Sine: Returns the sine of an angle.
Sinh: Returns the hyperbolic sine of a value.
Cos: Returns the cosine of an angle.
Cosh: Returns the hyperbolic cosine of a value.
Tan: Returns the tangent of an angle.
Arcsin: Returns the inverse sine (angle whose sine is x).
Arcsinh: Returns the inverse hyperbolic sine.
Arccos: Returns the inverse cosine (angle whose cosine is x).
Arccosh: Returns the inverse hyperbolic cosine.
Arctan: Returns the inverse tangent (angle whose tangent is x).
Arctanh: Returns the inverse hyperbolic tangent.
Arctan2: Returns the angle from x and y coordinates, resolving full quadrants.
Logarithm: Calculates the natural logarithm (ln) of a value.
Log1p: Calculates ln(1 + x) for improved precision with small x.
Log2: Returns the base-2 logarithm of a value.
Log10: Returns the base-10 logarithm of a value.
Exponential: Returns e raised to the power of a value.
Expm1: Returns e^x − 1, precise for small x.
Average: Computes the mean of a set of numbers.
Hypot: Returns the Euclidean distance √(x² + y²) for 2D or 3D inputs.
Opposite: Returns the negative of a number (−x).
DegToRad: Converts degrees to radians.
RadToDeg: Converts radians to degrees.
StringToNumber: Converts a text string into a numeric value.
NumberToString: Converts a number into a text string.
Boolean Converter: Converts a value to a boolean (true/false).
Boolean to Number: Converts a boolean to 1 (true) or 0 (false).
LN2: Natural logarithm of 2.
LN10: Base-10 logarithm of 10.
Log2e: Base-2 logarithm of e.
Log10e: Base-10 logarithm of e.
E: Euler’s number (≈2.71828).
Pi: π (≈3.14159).
Sqrt(1/2): Square root of 1/2.
Sqrt2: Square root of 2.
Sqrt3: Square root of 3.