Curve analysis nodes evaluate curve properties such as length, continuity, tangents, and curvature.
All the nodes are explained below.

Checks whether a curve’s start and end points coincide, confirming if it forms a complete loop.
Calculates the total length of a curve by measuring its full path.
Returns the curve parameter (t-value) that corresponds to a specific measured length along the curve.
Computes the area enclosed by a closed curve, treating it as a planar boundary. Returns a number.
Finds the midpoint of a curve by evaluating it halfway along its length.
Extracts the start point and end point of a curve, useful for connections or direction analysis.
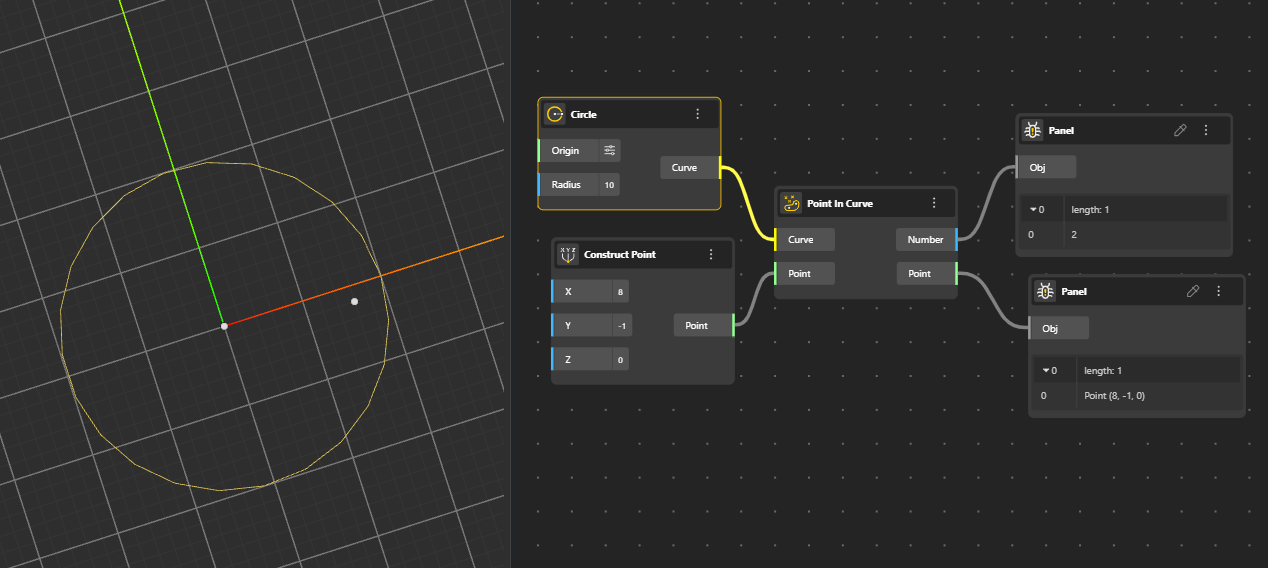
Returns a point located at a specified curve parameter, giving precise positional evaluation.
Parameter: Finds the exact point along a curve by specifying a parameter value between 0 (start) and 1 (end).
Identifies a point lying on the curve. Output ports:
Number: Returns 0,1, or 2.
Point/Region relationship: 0 = outside, 1 = coincident, 2 = inside
Point: Return the Point.
Retrieves the underlying control points that define a NURBS or spline curve’s shape. Output Port:
Point: Returns the position of the control point that defines the curve’s shape.
Knots: Returns the values that determine how the curve transitions between control points.
Weight: Returns the influence of the control point on the curve’s form.
Breaks an arc into its basic components: Plane, Radius, Angle 1 (start angle) and Angle 2 (end angle)
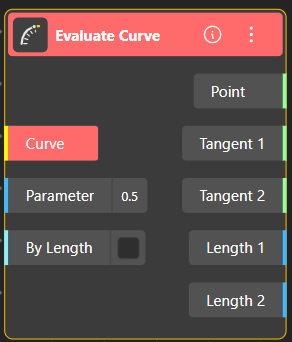
The Evaluate Curve node allows you to extract detailed geometric information from any point along a curve. You can evaluate the curve either by its parameter value (typically between 0 and 1) or by a specific curve length.
Inputs:
Curve: The curve you want to evaluate.
Parameter: A value (usually 0–1) that represents a position along the curve. For example, 0.5 returns the midpoint.
By Length (toggle): When enabled, the node interprets the input as a length value instead of a parameter.
If ON → the number you enter corresponds to length along the curve.
If OFF → the number corresponds to a parameter value.
Outputs:
Point: The exact point on the curve at the selected parameter or length.
Tangent 1 / Tangent 2: The tangent vectors at that point, giving the direction of the curve.
Length 1 / Length 2:
Length 1: Length of the curve segment from the start to the evaluated point.
Length 2: Remaining length from the evaluated point to the end of the curve.
Checks whether an entire curve lies on a single geometric plane.
Finds the closest point on the curve to a given reference point.
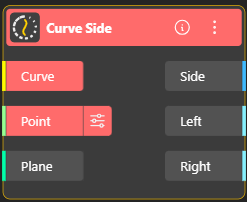
Determines which side of the curve the input point lies on, based on orientation or direction. Output port:
Side: Side of curve on which point was found (-1=Left, 0=Coincident, +1=Right)
Left: Boolean Output (True/False)
Right: Boolean Output (True/False)
Detects locations where a curve is not smooth, such as sharp corners, kinks, or breaks in continuity. Returns all points of Discontinuity.