Boolean (in geometry) simply means combining shapes using logic like adding them together, cutting one from another, or keeping only the parts where they overlap. Boolean operation nodes combine or separate geometry using union, difference, intersection, and splitting methods.

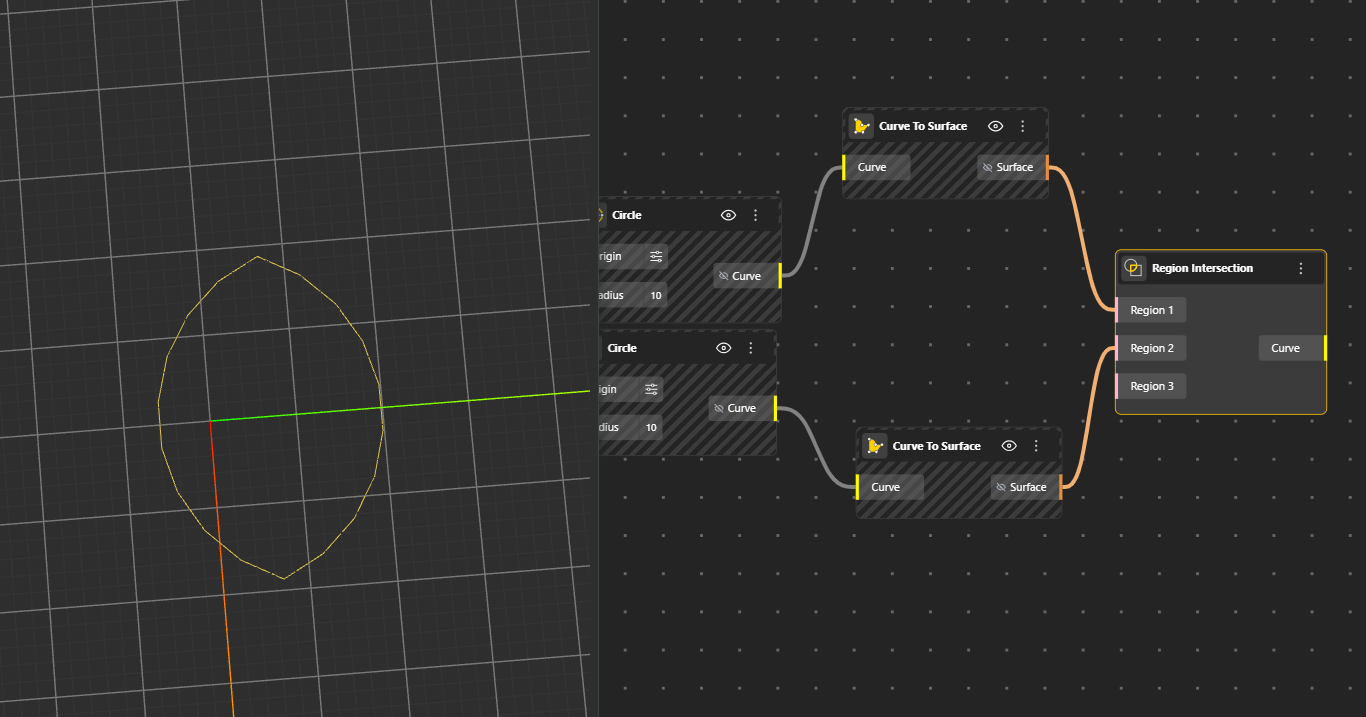
Finds the overlapping area between two or more 2D regions (closed curves). The output is only the shared portion where all regions cover the same space. Hide the original geometry nodes for better preview.
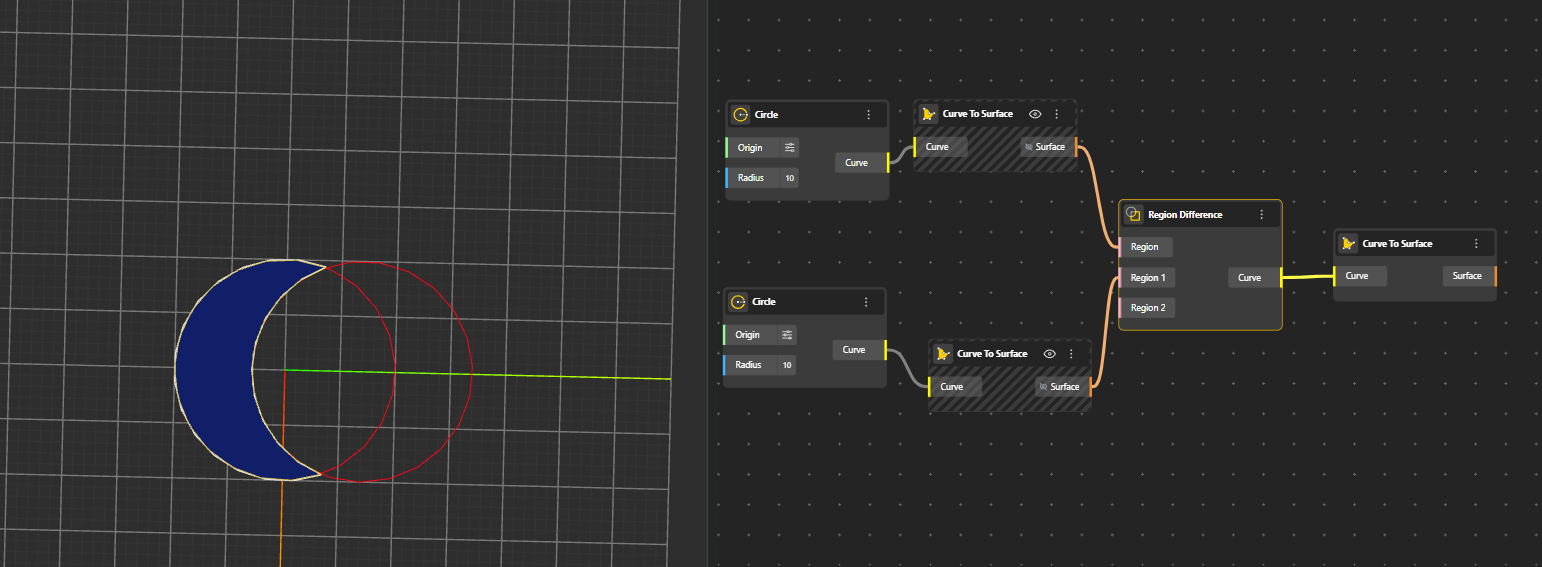
Subtracts one region from another. It keeps the first region and removes the area that overlaps with the second region. Generates Curve. Hide the original geometry nodes for better preview.
Region 1 is the main region you want to keep. Region 2 and onwards - regions that will be cut out from the main region if connected.
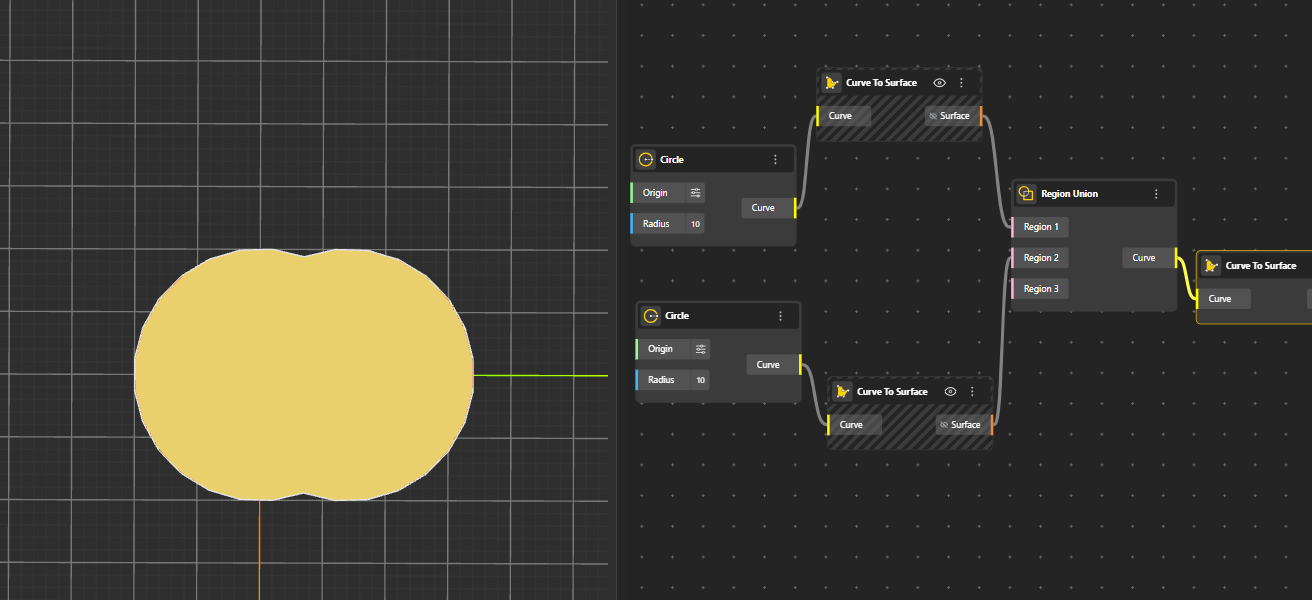
Merges multiple 2D regions into a single combined region. Overlapping or touching boundaries are fused into one clean shape. Generates Curve. Hide the original geometry nodes for better preview.
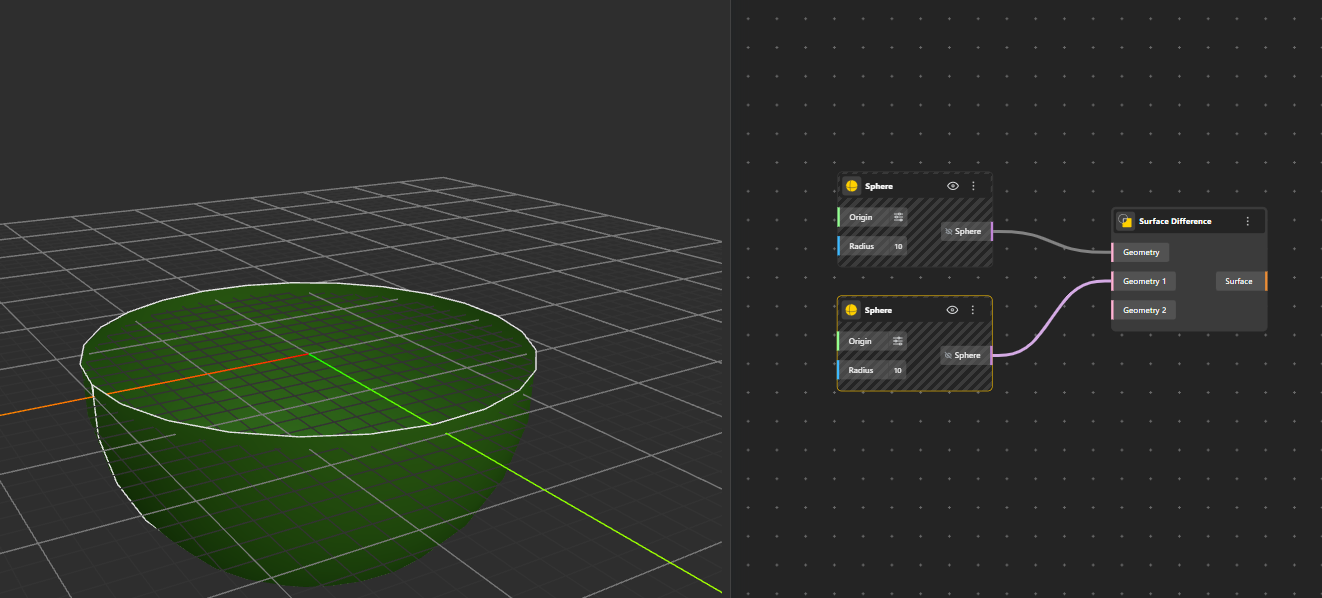
Subtracts one surface from another. The first surface is trimmed by removing the area where the second surface overlaps. Generates Surface. Hide the original geometry nodes for better preview.
Geometry 1 is the main region you want to keep. Geometry 2 and onwards will be cut out from the main geometry if connected.
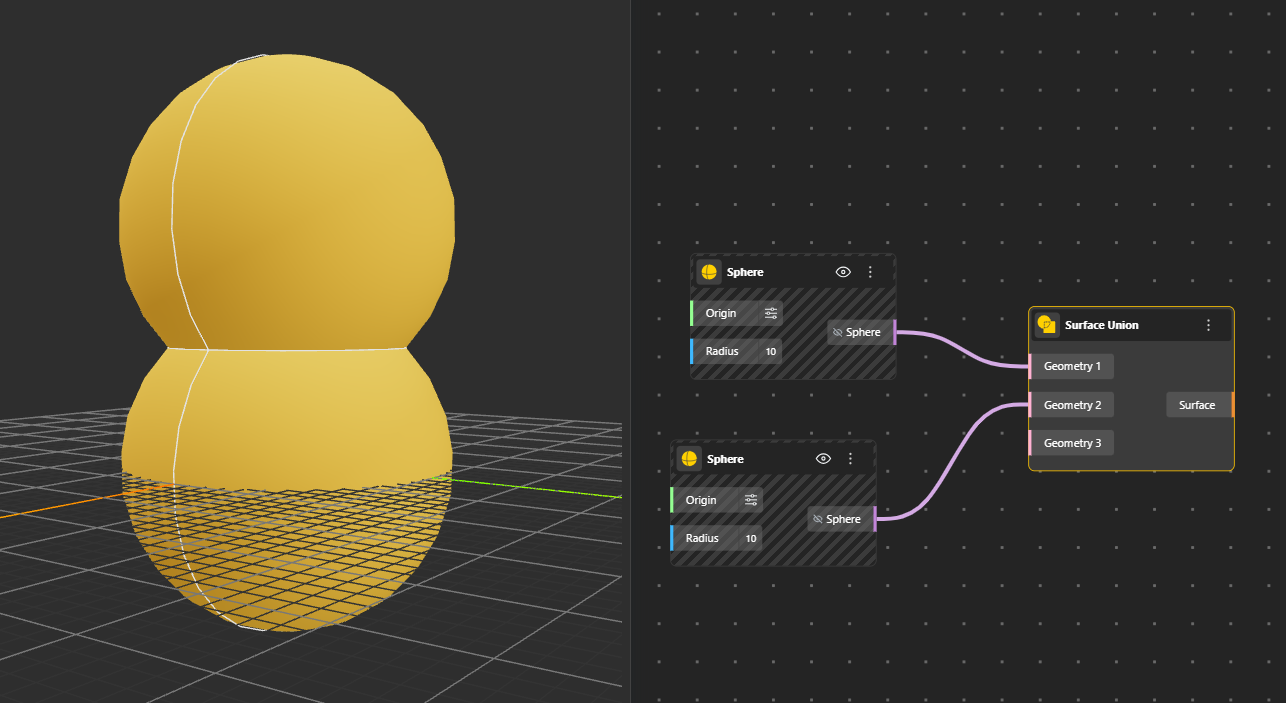
Combines two or more surfaces into one unified surface. This creates a single connected surface from overlapping or adjacent inputs. Generates Surface. Hide the original geometry nodes for better preview.
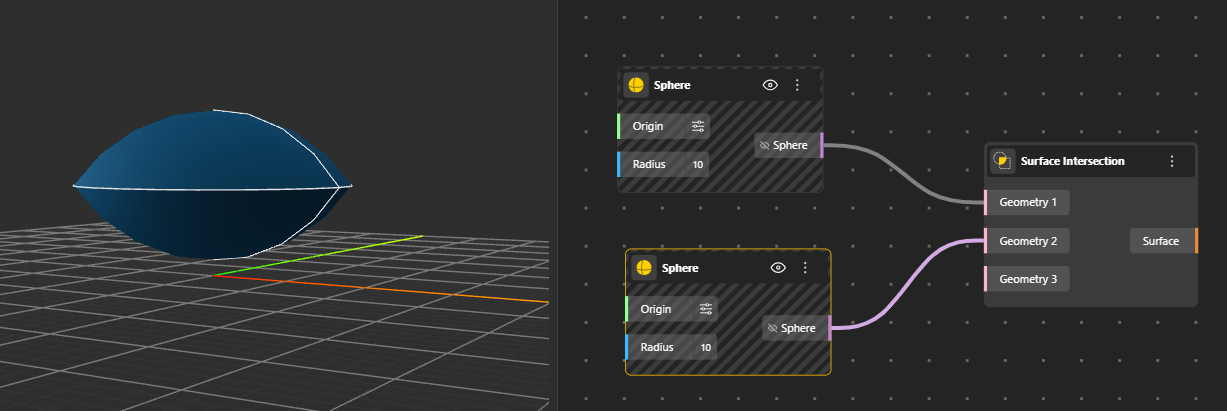
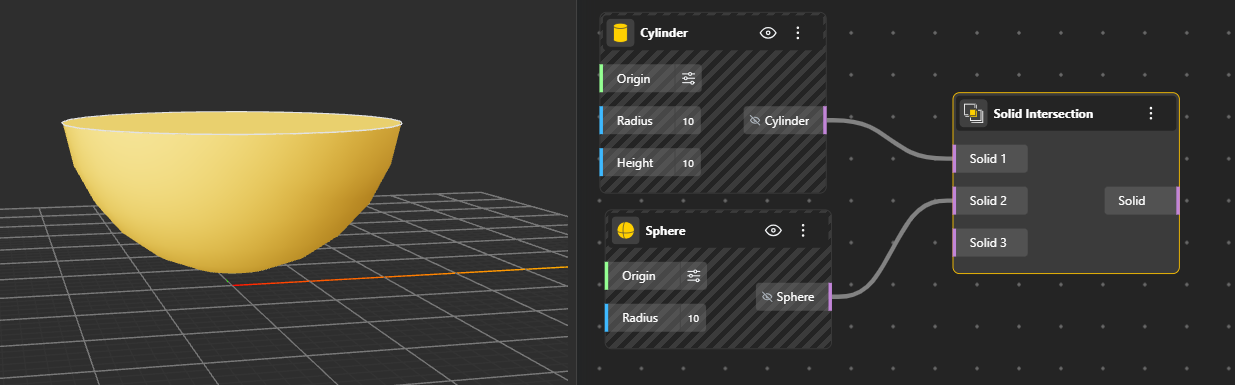
Calculates the shared area or intersection curve between two surfaces. The output represents the exact portion where the surfaces cross or overlap. Generates Surface. Hide the original geometry nodes for better preview.
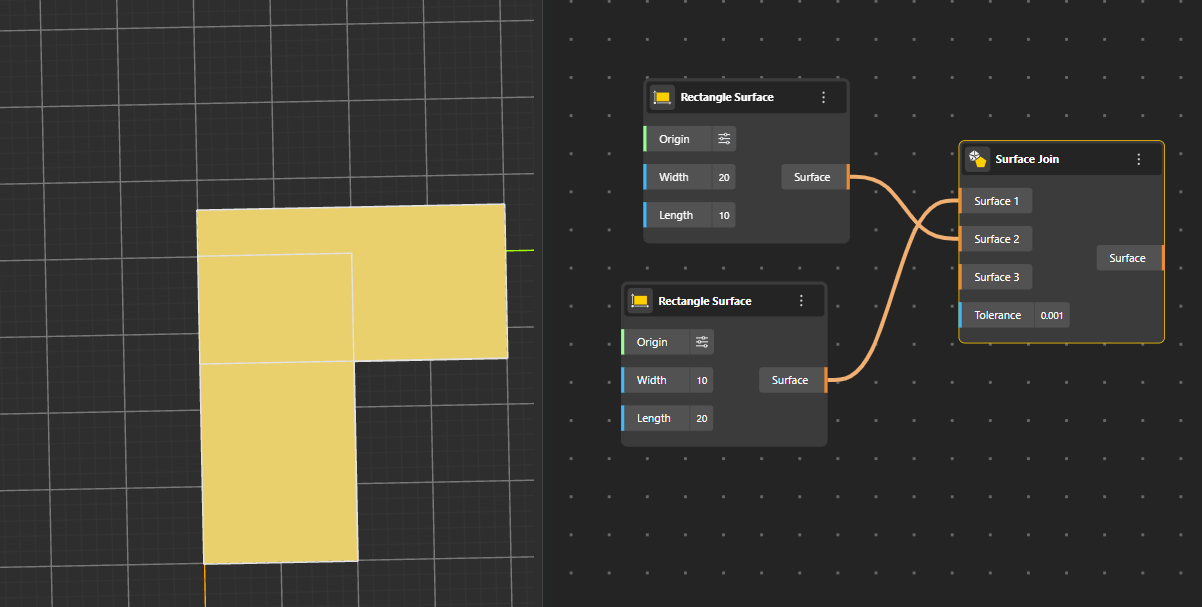
Merges multiple surfaces edge-to-edge into one connected surface. It creates a single surface structure without smoothing or blending.
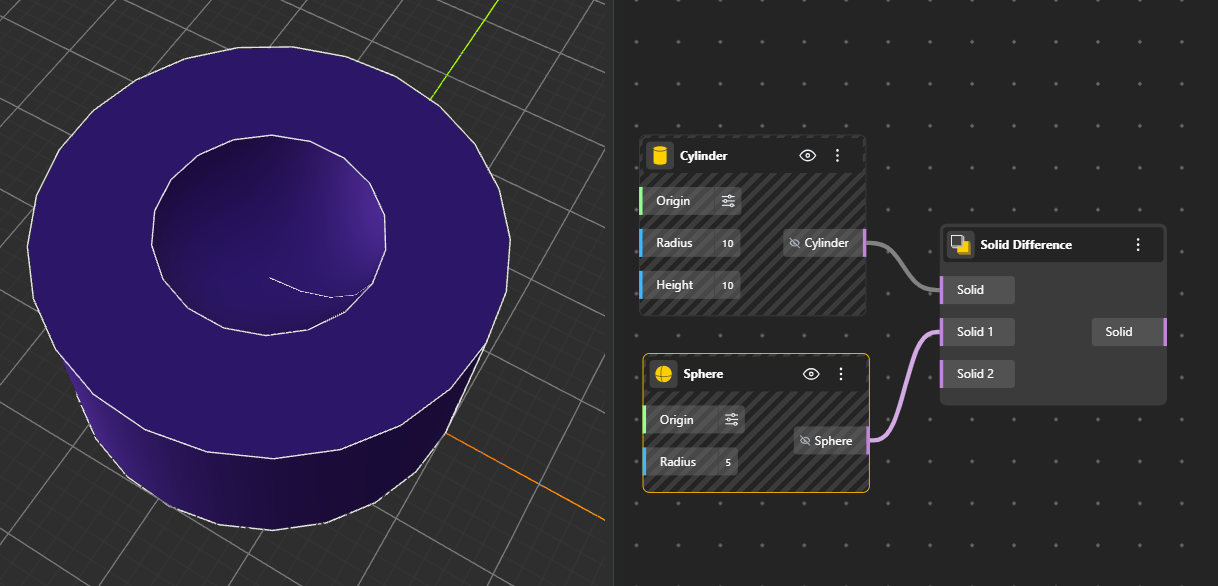
Subtracts one solid from another. The resulting solid keeps the shape of the first input but removes any volume overlapping with the second. Hide the original geometry nodes for better preview.
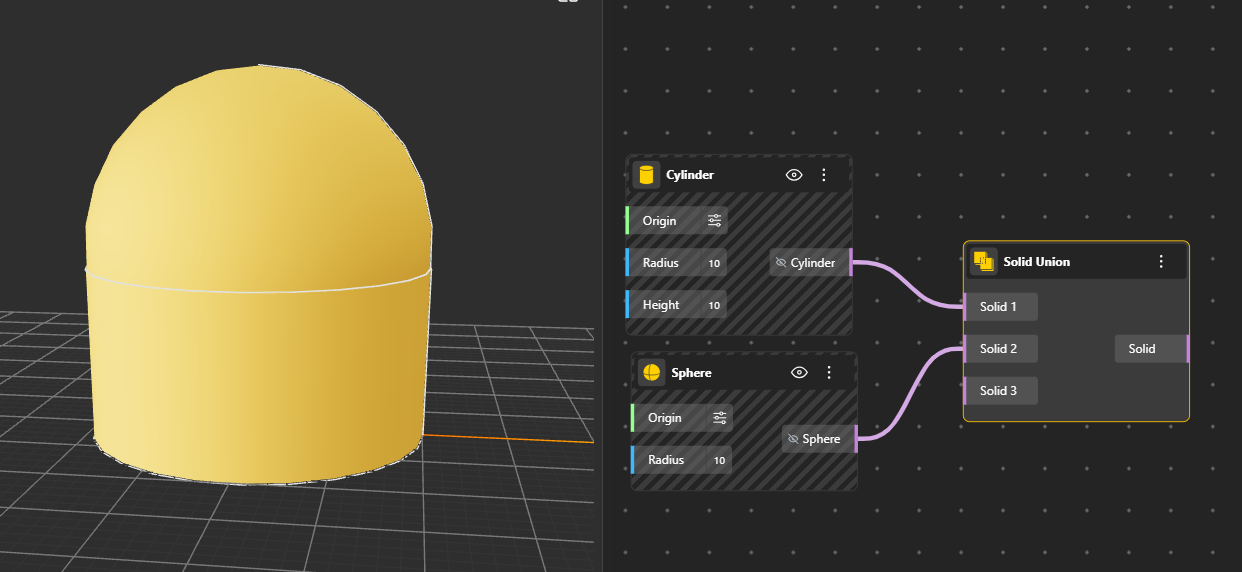
Combines multiple solids into a single clean 3D volume. Any touching or overlapping areas are merged into one solid body. Hide the original geometry nodes for better preview.
Returns only the 3D volume shared by all input solids. The output is the overlapping portion where the solids occupy the same space. Hide the original geometry nodes for better preview.
Cuts a solid using another solid or surface as a cutter. The output contains all the separated pieces created from the cut.
Splits a single solid using multiple cutters at once. It returns all fragments generated from every cutting operation.
Cuts a surface using one or more curves or surfaces. The result is a set of smaller surface pieces created from the split.