Solid nodes create, deconstruct, and analyze 3D volumetric geometry for modeling and fabrication.
Creates a box by defining its center point and dimensions (width, depth, height). The box expands equally in all directions from the center.
Generates a box using a base plane and size parameters. A simple way to create standard rectangular solids.
Creates a box by selecting two opposite corner points. The box is formed between these two points, defining its full volume.
Generates a sphere using a center point and a radius value.
Creates a cylinder from a base plane, radius, and height. Can be used for columns, pipes, and round solids.
Generates a donut-shaped 3D solid defined by a major radius (ring size) and minor radius (tube thickness).
Creates a cone using a base plane, radius, and height. Useful for shapes that taper to a point.
Creates a classic pyramid solid by defining its origin, base width, base length, and height. Useful as a clean primitive for quick massing studies, geometric exploration, and base parametric forms.
Generates a pyramid with a flat top by independently controlling base and top dimensions along with height. Ideal for producing tapered volumes, stepped forms, and fabrication-ready architectural or product geometries.
Constructs a sphere that fits through four non-collinear points. The sphere is calculated so all four points lie on its surface.
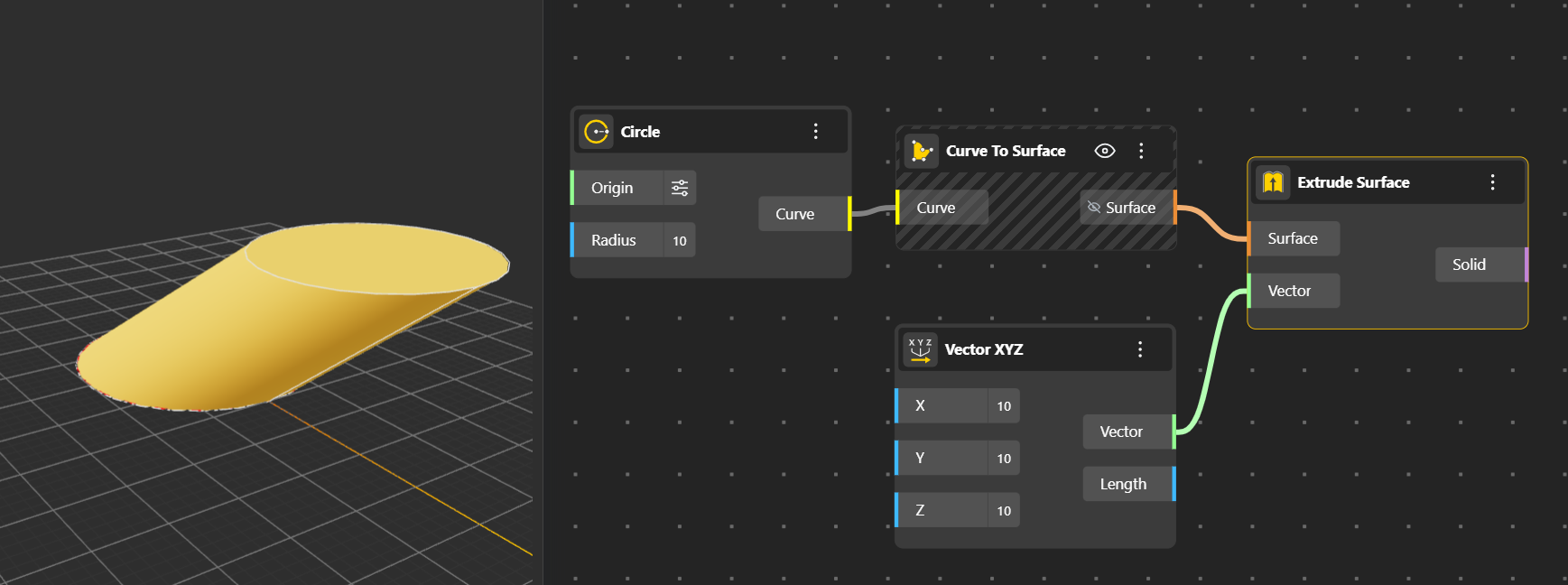
Turns a 2D surface or curve into a 3D solid by extending it in a specified direction or distance.
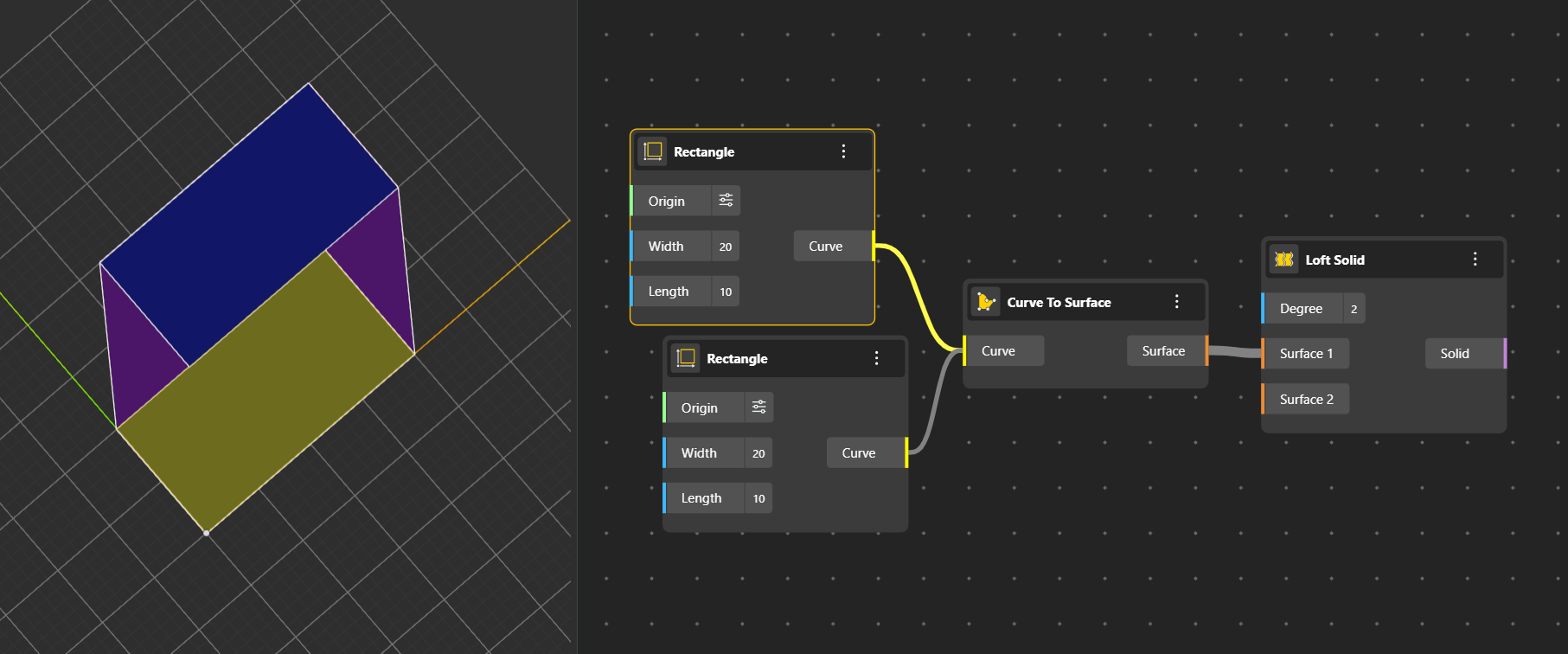
Creates a solid by lofting between two or more curves or surfaces. Smoothly blends shapes along a path. Here the purple surfaces show the path used to combine the two rectangles.
Calculates the surface area of a solid. Useful for fabrication, material estimation, and geometry analysis.
Computes the internal volume of a solid. Helpful for simulations, massing studies, or calculating capacity.
Extracts iso-parametric curves from the surfaces of a solid. These curves follow the U and V directions of the solid’s underlying geometry.
Outputs the edge curves that define the boundary of a solid or surface. Useful for trimming, reconstructing, or analyzing geometry.
Extracts the 8 corner points of a box. These points can be used for connections, references, or further modeling logic.
Returns key information about a box, such as its size, center, corner points, and orientation.
Breaks a solid into its elemental parts: faces, edges, and vertices. Allows deeper analysis or reconstruction of geometry.
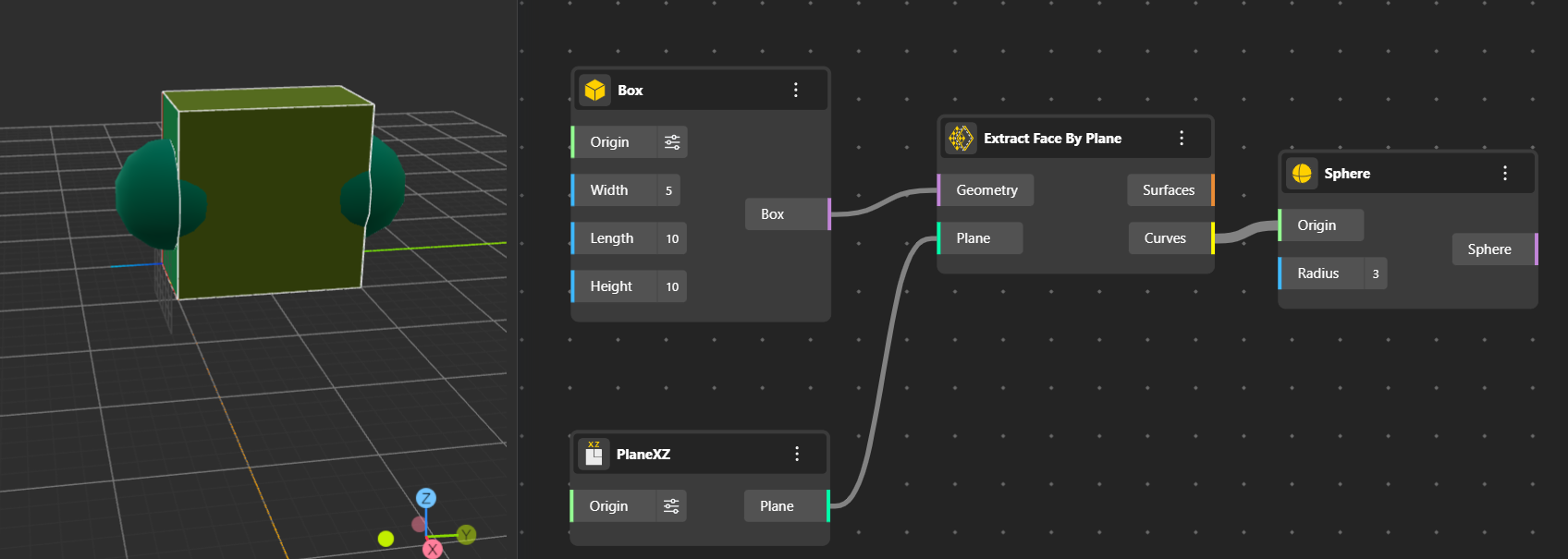
Selects and outputs the face of a solid that is aligned to a given plane. The node pushes your shape outward in the direction of a plane you choose. Anything you connect to its output will sit perfectly on that same plane. Helpful for isolating specific surfaces.
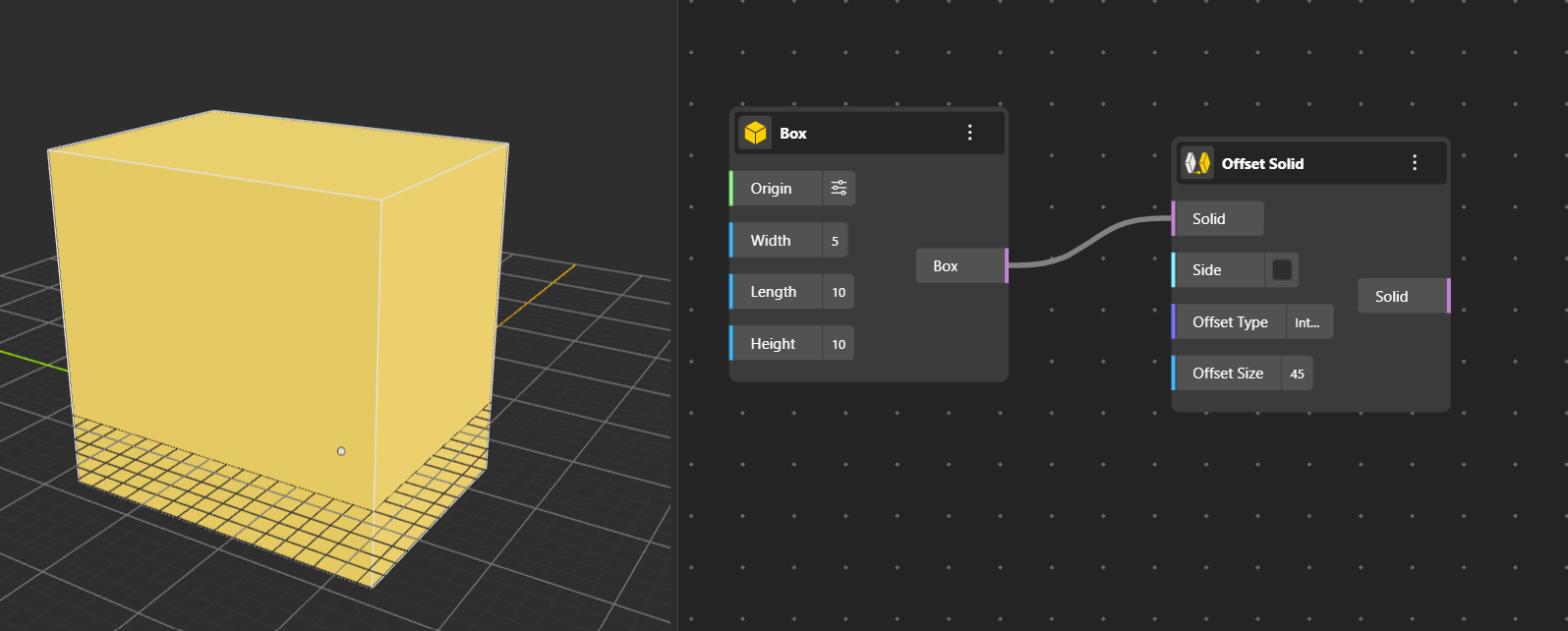
Creates an enlarged or shrunken version of a solid by offsetting its surfaces inward or outward by a specified distance. Offset type can be only "Arc", "Tangent" or "Intersection". It is default "Arc".