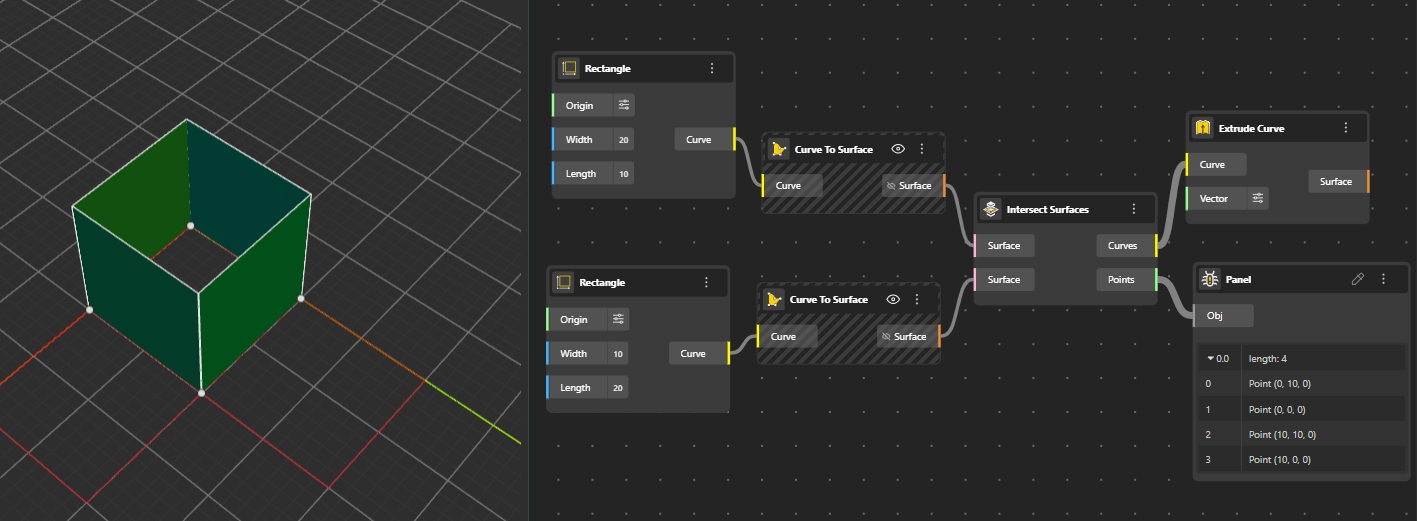
Intersection nodes help you find the exact locations where different geometries interact. Whether you’re intersecting curves, surfaces, or solids, these tools extract meaningful outputs such as intersection points, overlap regions, or split segments. They are essential for accurate modeling, Boolean logic and creating geometry driven by precise spatial relationships.

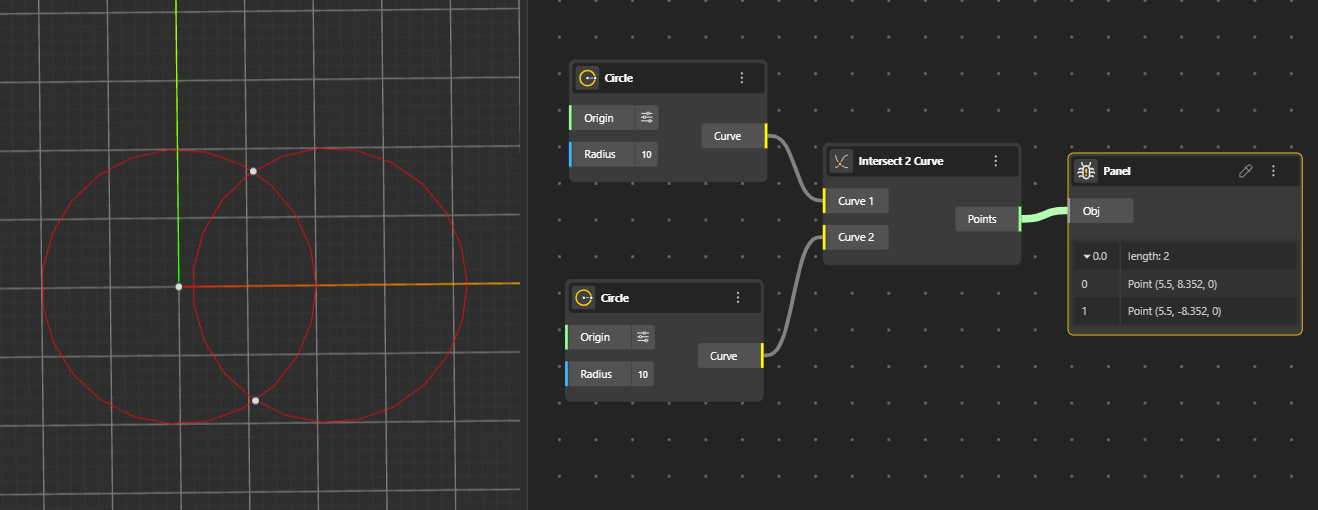
Finds the points where two curves cross each other. Outputs a list of intersection points.
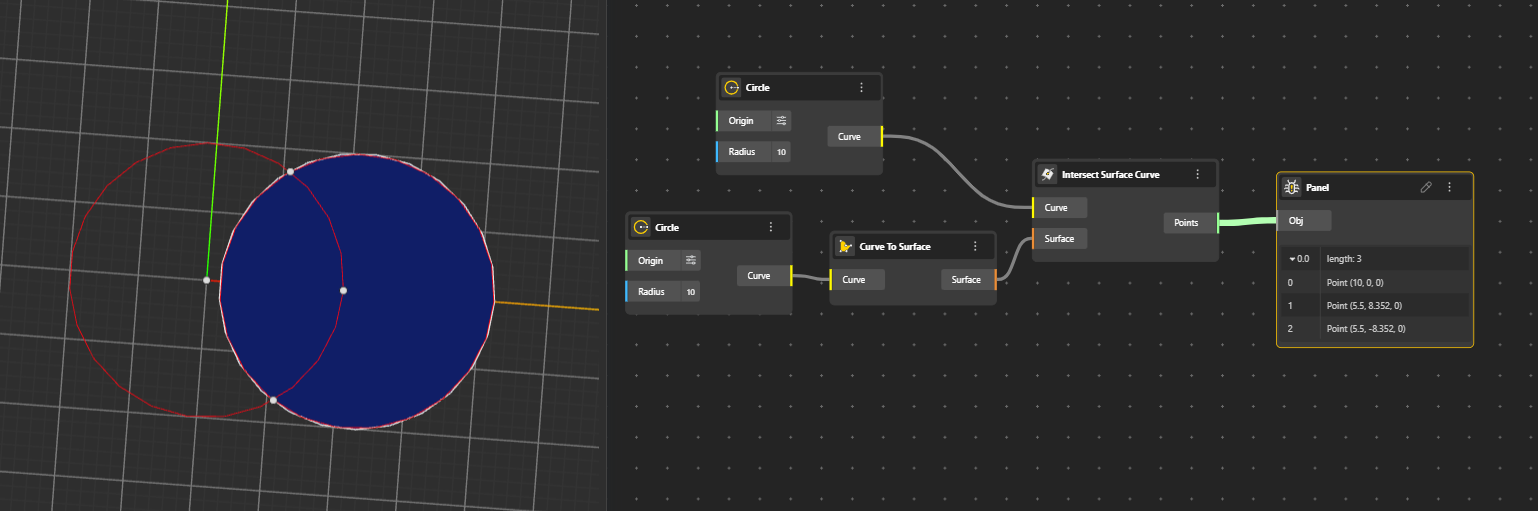
Calculates the intersection between a surface and a curve. Returns the curve or points where the input curve intersects the surface.
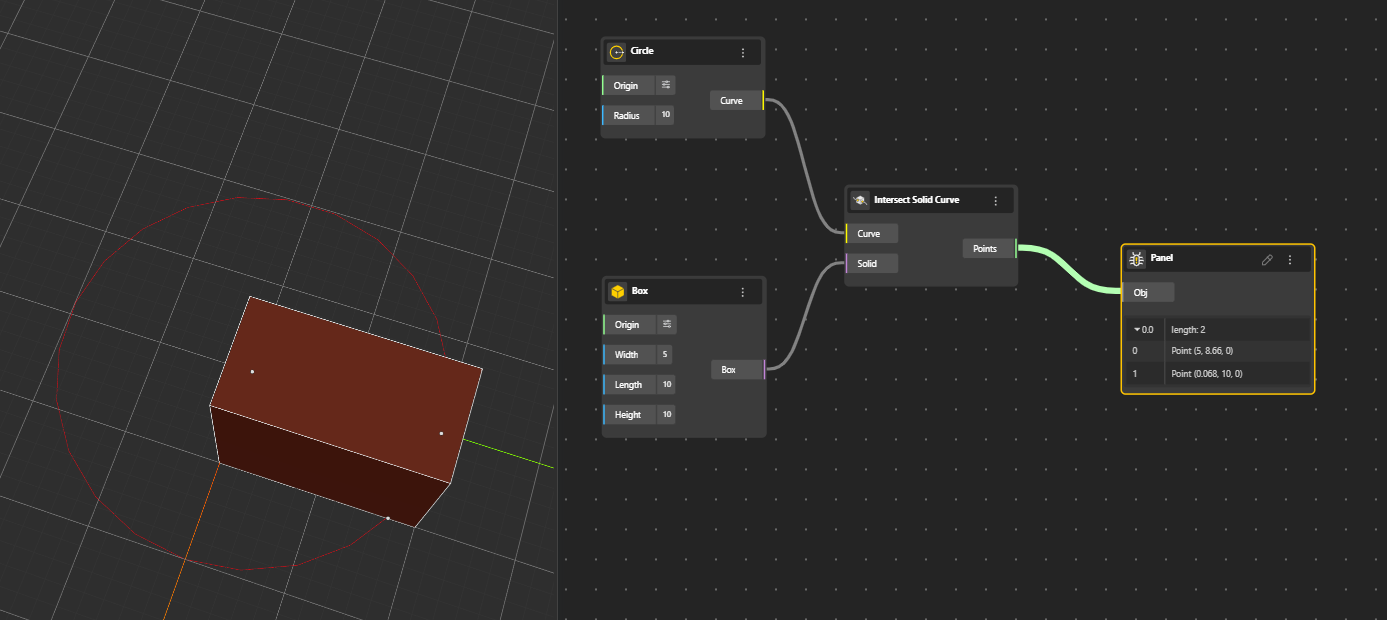
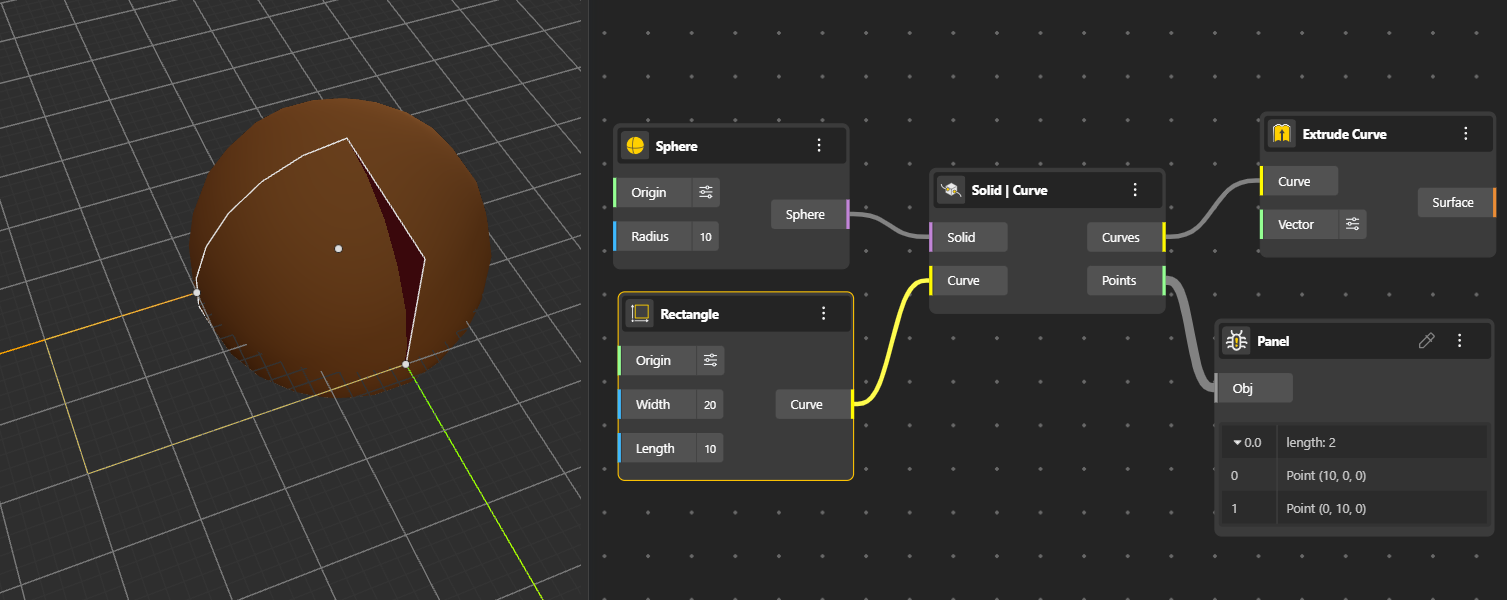
Finds the intersection between a solid and a curve. Outputs the points and curves where the curve intersects the solid.
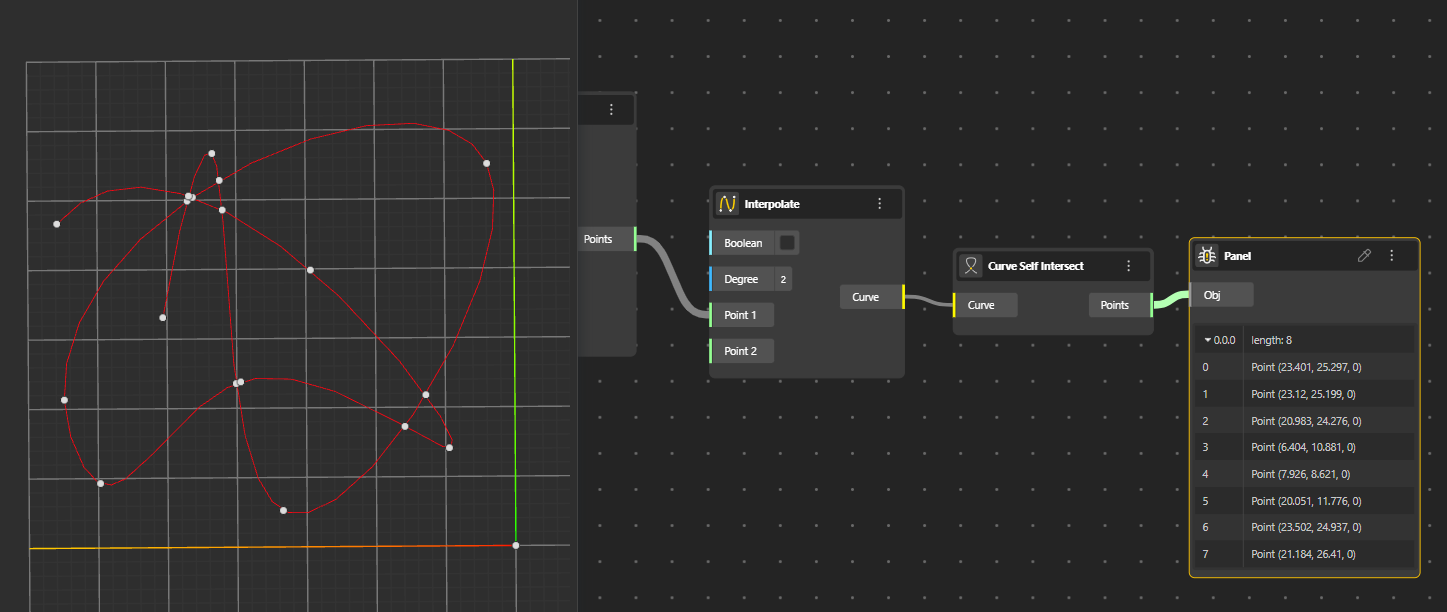
Detects points where a single curve crosses itself. Useful for analyzing loops or overlapping sections of a curve.
The output provides intersection points and curves on the faces where the solid and curve meet. (Hide the Solid node for better preview.)
The output gives the intersection curves and points on the solid’s face in the direction of the plane.
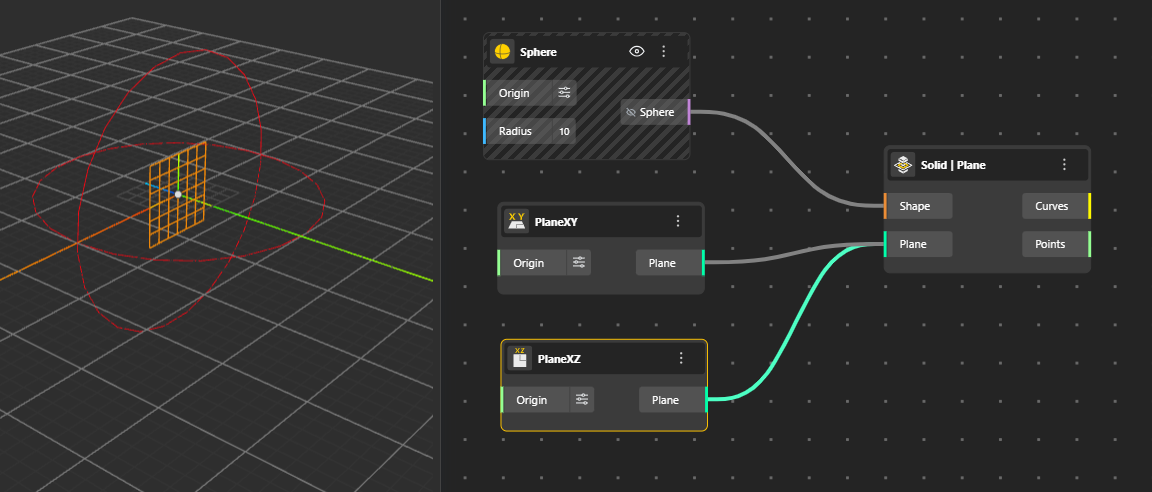
Finds the intersection line between two planes. The output is given by a single line representing where the two planes cross.
Calculates the intersection curves between two surfaces. The output are the curves that represent the exact lines where the surfaces intersect. (You can Hide the surfaces for better preview)