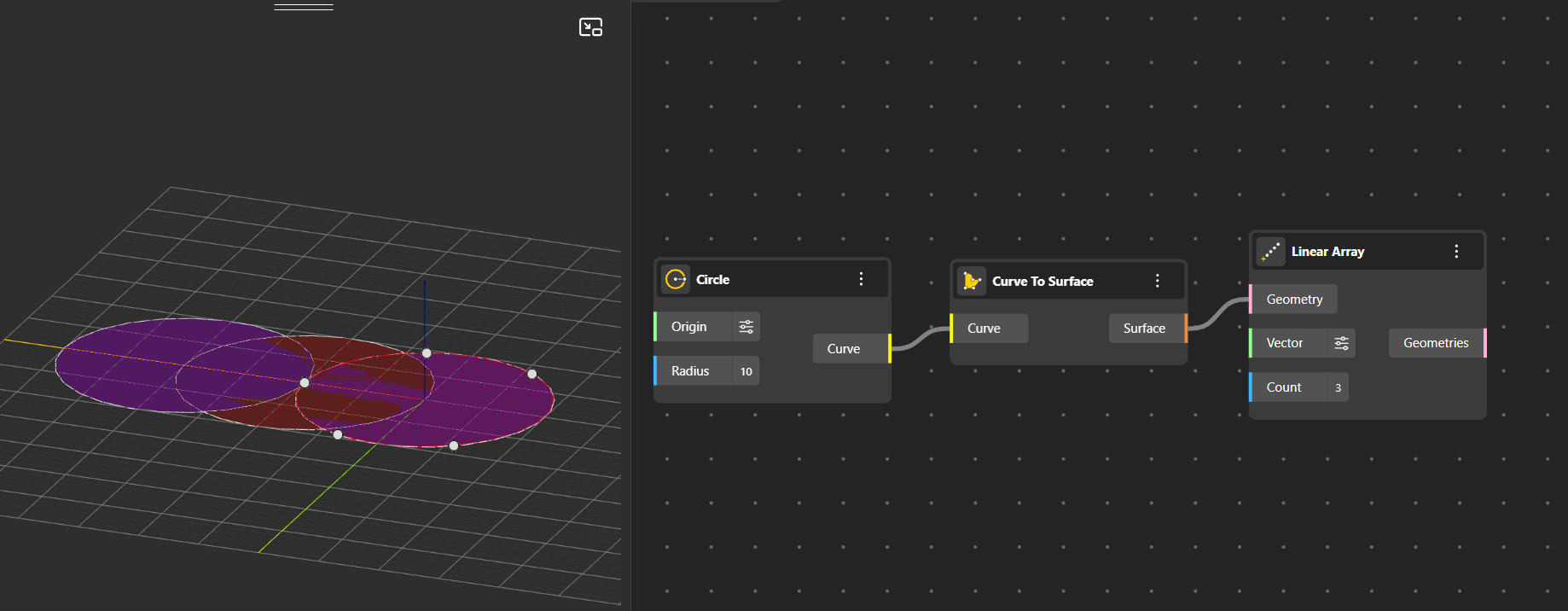
Linear Array: Creates multiple copies of an object in a straight line along a specified direction, with uniform spacing between instances. You can set the direction using the vector input (default is the X-axis) and control how many copies are generated using the count input.
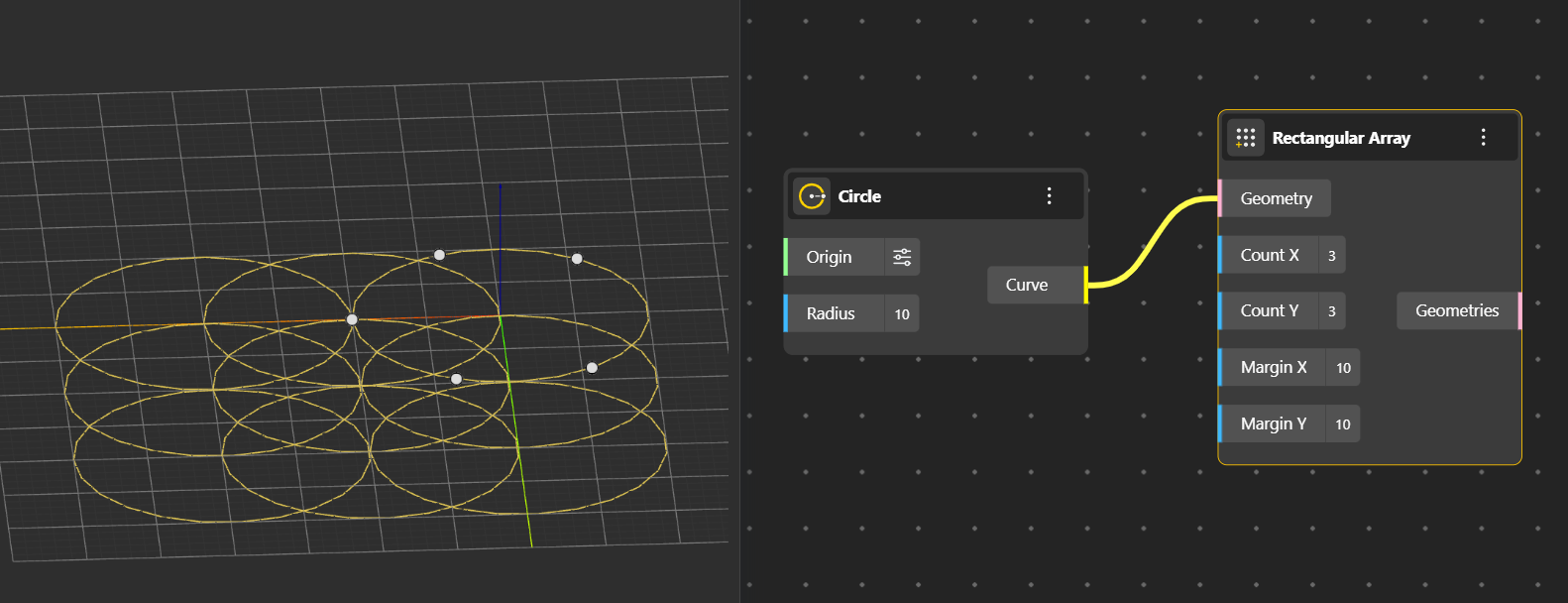
Rectangular Array: Generates copies of an object in a 2D grid pattern (along the X-Y plane). You can change the spacing and count in both directions using the Margin X or Y and Count X or Y respectively.
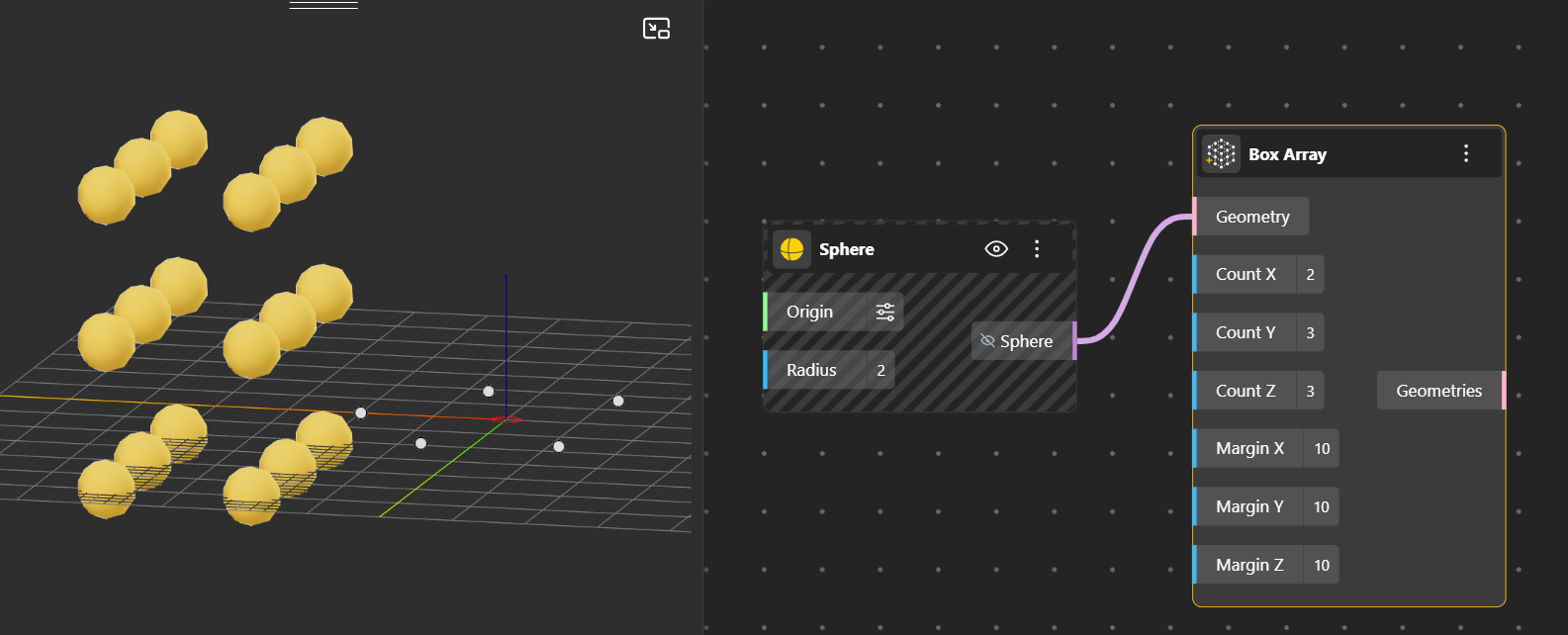
Box Array: Creates copies of an object arranged inside a 3D box volume. You can control the count and the distance along X, Y, and Z axes using Count and Margin respectively.
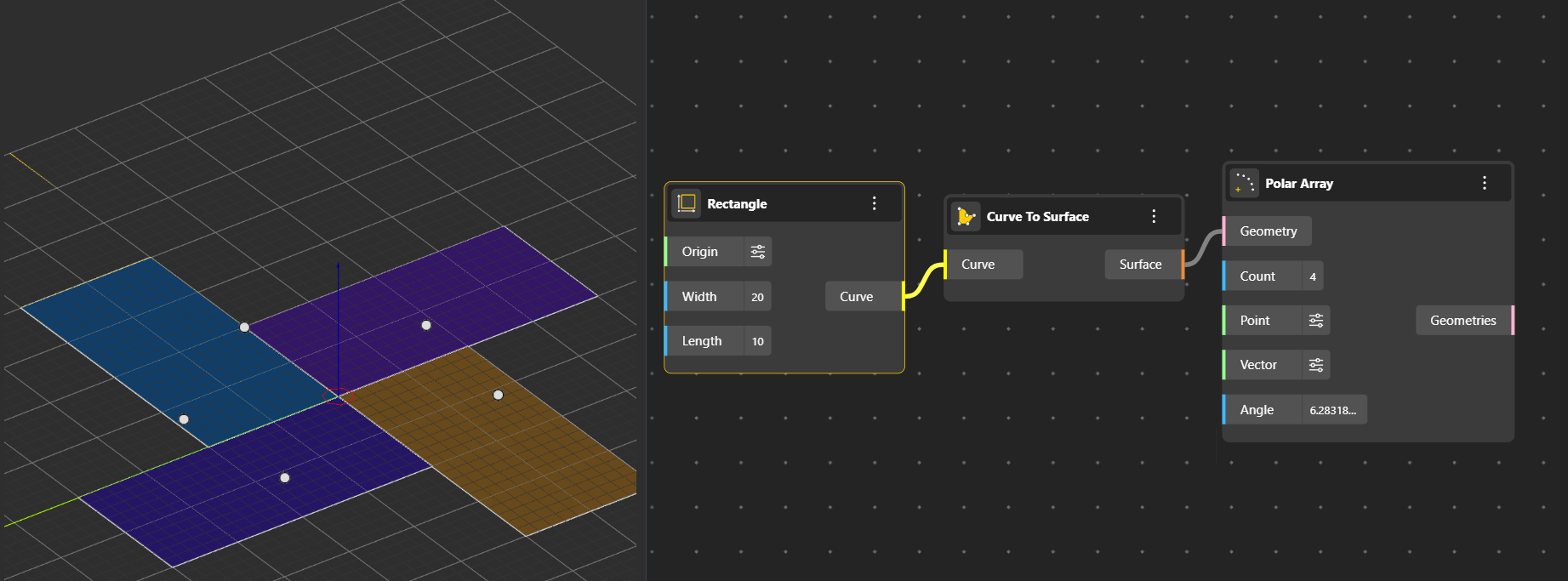
Polar Array: Distributes multiple copies of an object around a central point in a circular pattern. You can specify the number of copies and the rotation angle.
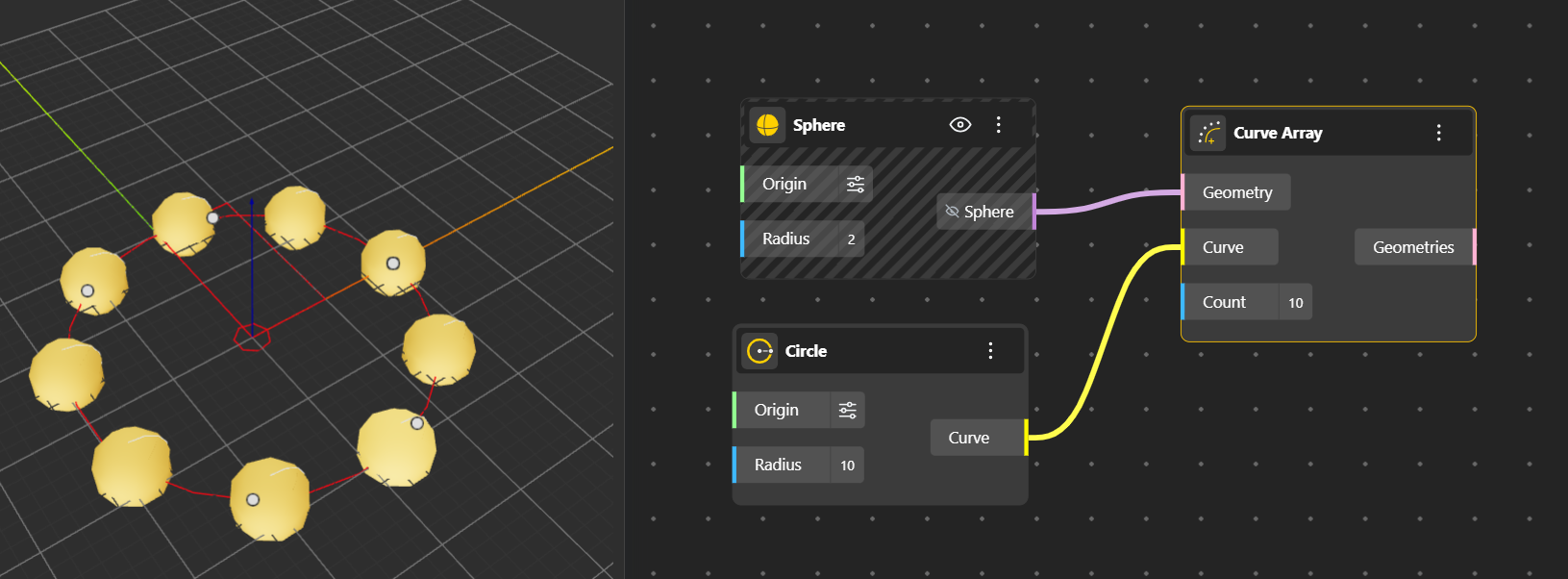
Curve Array: Places copies of an geometry along a curve at specified intervals or normalized positions. The object follow the curve’s orientation.
Populate 2D: Randomly distributes points across a 2D surface or region. Useful for procedural placement of geometry or patterns.
Populate 3D: Randomly distributes points within a 3D volume. Ideal for creating volumetric arrangements or particle-like distributions.
Populate Geometry: Distributes points over an input geometry (surface or curve) either randomly or according to specified patterns. These points can then be used to place objects.
Hexagonal Grid: Generates a grid of points or objects arranged in a hexagonal (honeycomb) pattern. Useful for tessellation or repeating structures.
Rectangular Grid: Creates a regular grid of points or objects in a rectangular layout on a plane. Allows control over spacing and number of rows and columns.
Square Grid: A special case of the rectangular grid where the spacing is equal in both directions, forming perfect squares.

