Surface nodes in BeeGraphy allow you to create, modify, analyze, and transform surfaces with full parametric control. These tools form the foundation of many modeling workflows, whether you’re building architectural skins, organic forms, or technical components.
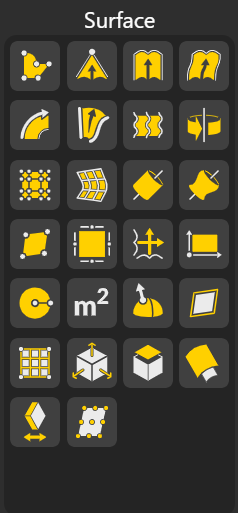
Converts a single curve into a surface by extending or filling it, giving a planar or ruled surface based on the curve’s shape.
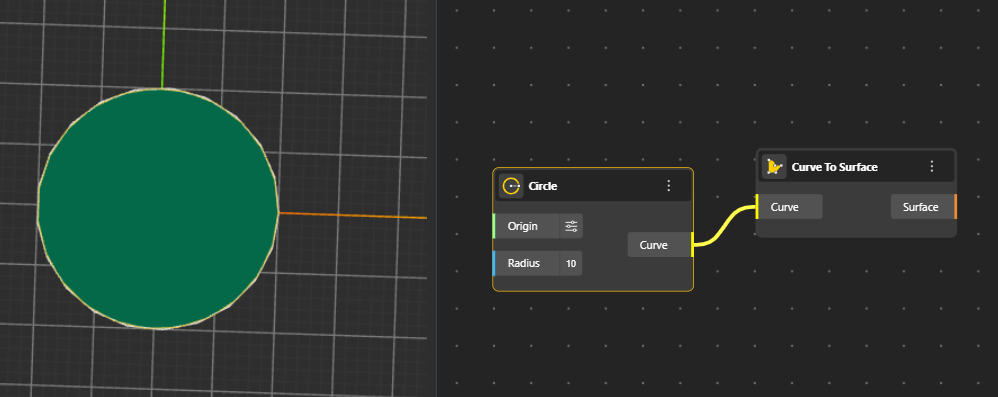
Creates a surface by pushing a point in a specified direction, forming a ruled surface that stretches from the original point.
Profile: The input curve that defines the direction and shape of the extrusion.
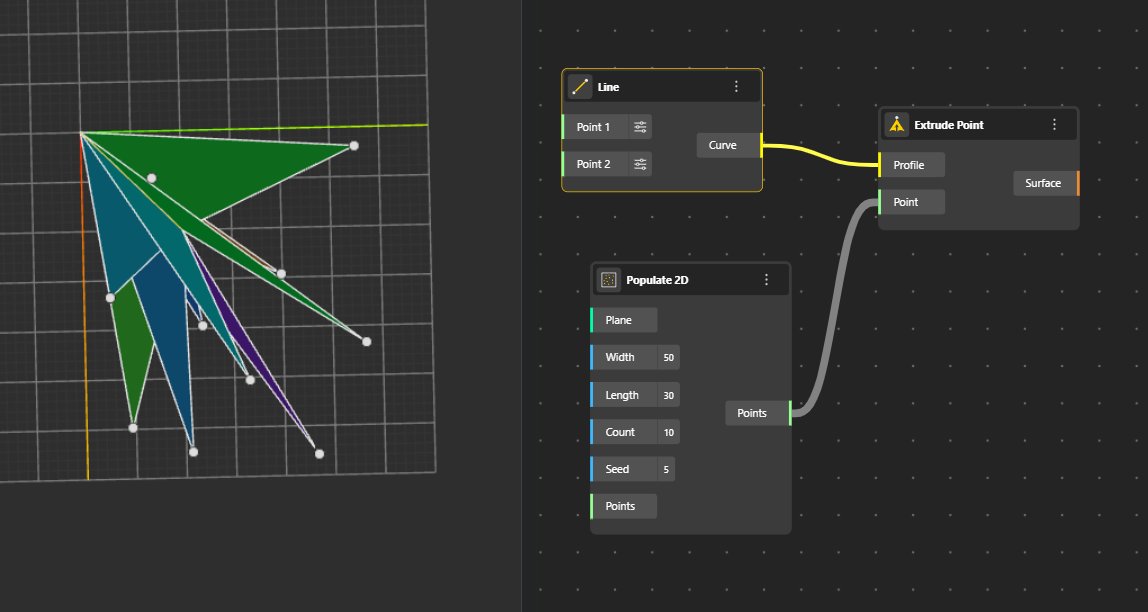
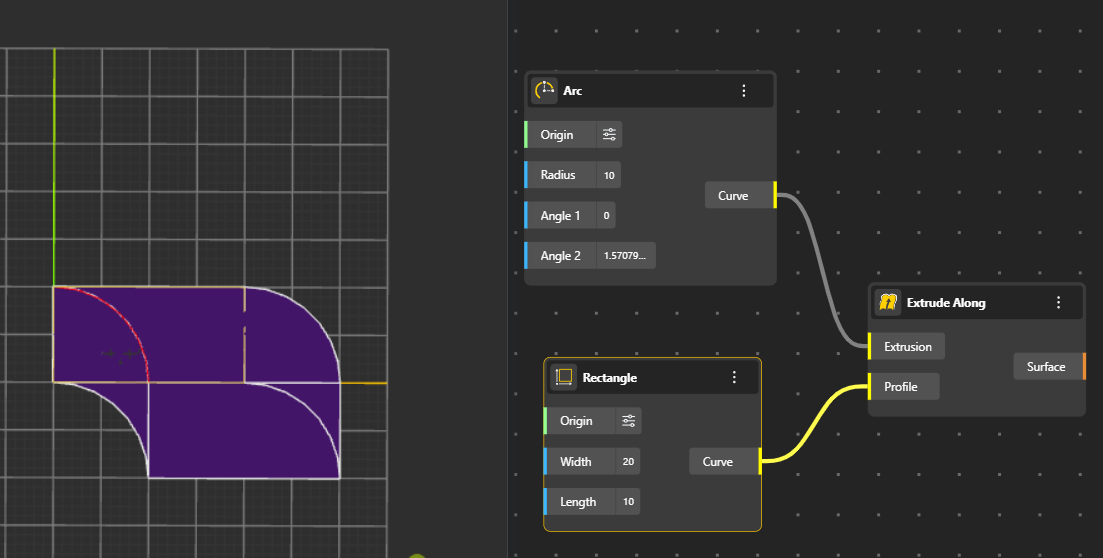
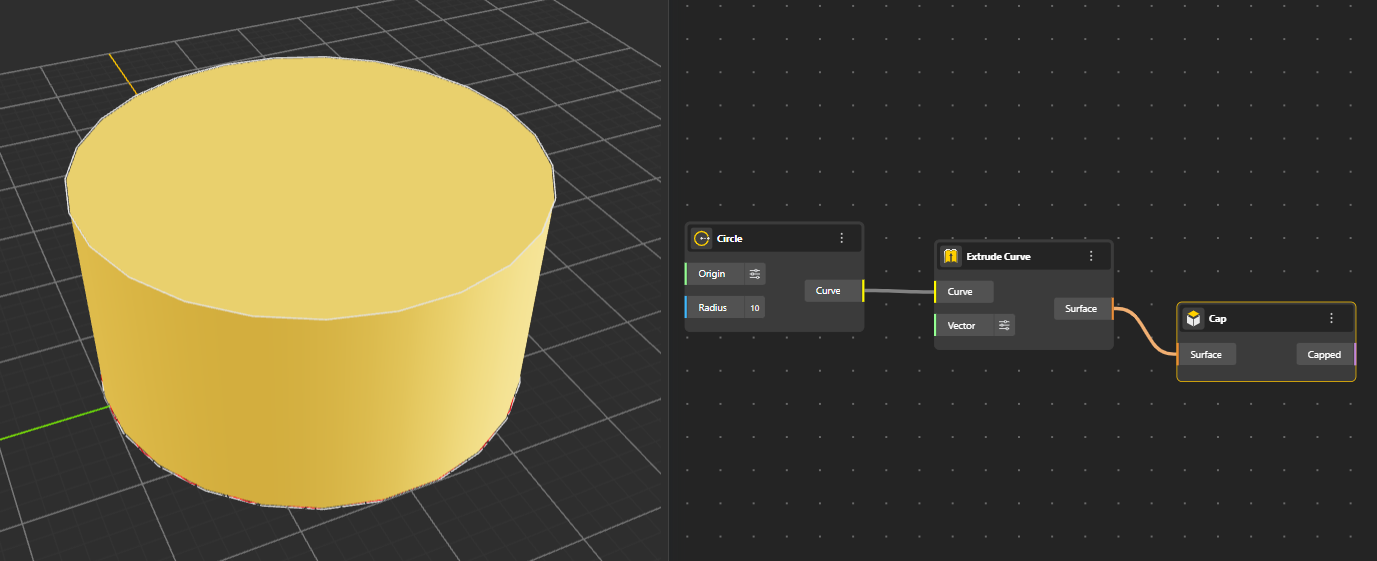
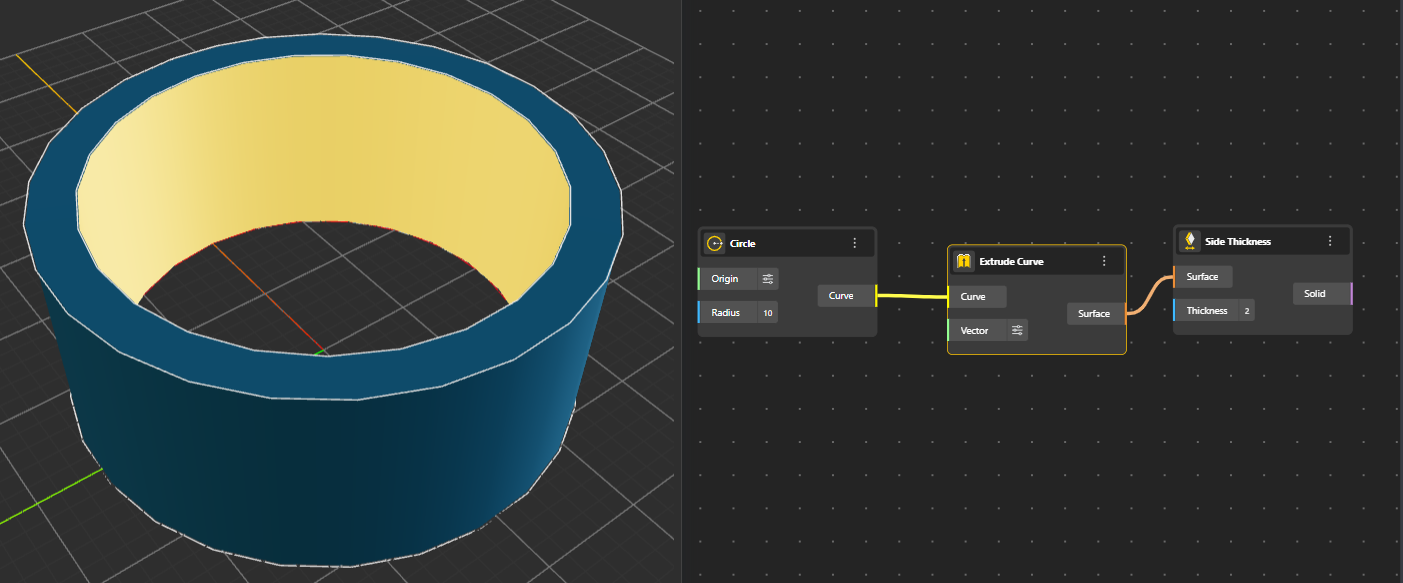
Generates a surface by extruding a curve along a direction or path, producing walls, panels, and linear extensions. You can decide the length and direction of extrusion from Vector port. (By default its In Z direction)
Extends geometry by following a guiding curve, allowing more controlled and organic extrusion paths.
Extrusion: The geometry or object that will be extended along the path.
Profile: The guiding curve or path that controls the direction and shape of the extrusion.
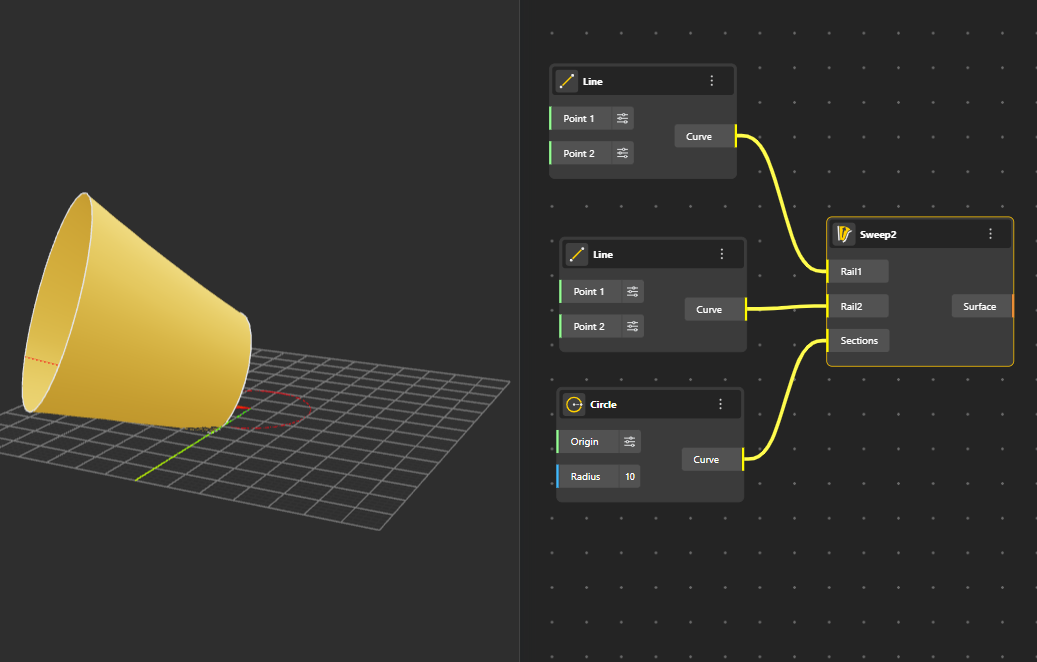
Creates a surface using two profile curves that are guided along a path or between additional guide curves for more complex shaping. All three curves must lie on different planes for the Geometry to generate
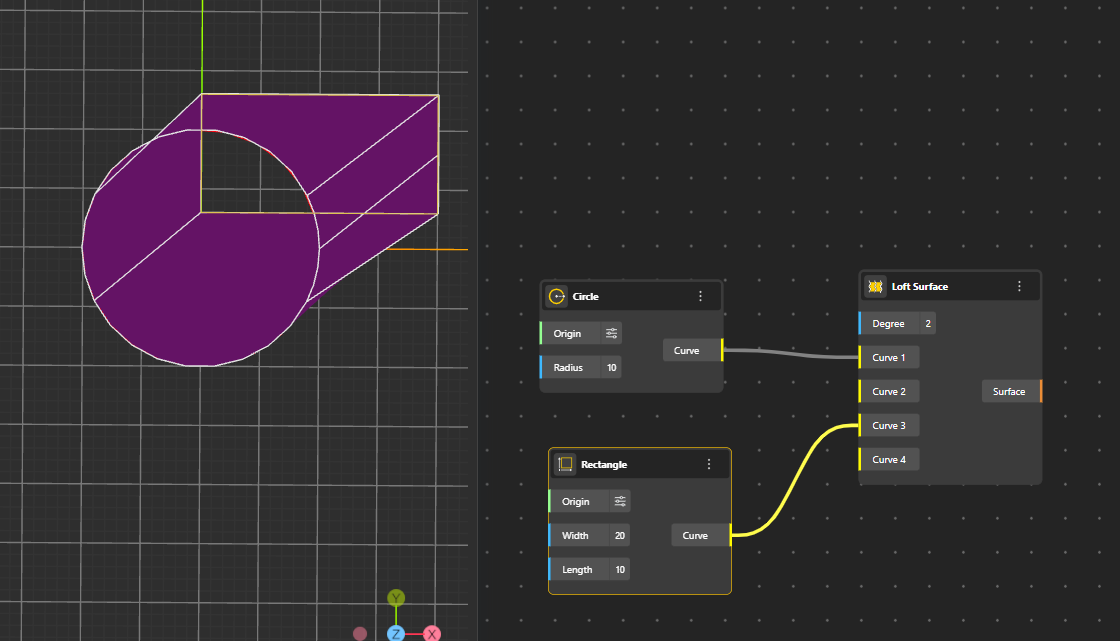
Creates a smooth surface by connecting several curves in order, blending them together into one continuous shape. The overlapping/common areas of the curves are not included in the final surface.
Degree: Controls how smooth or curved the loft becomes when connecting the shapes.
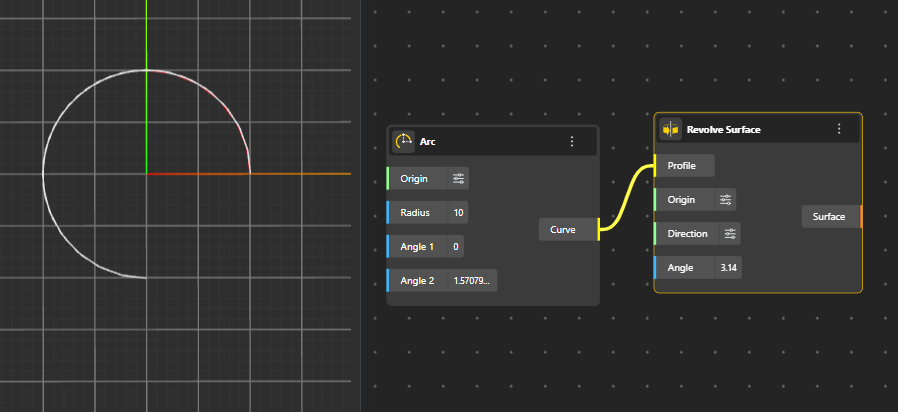
Generates a surface by rotating a curve around an axis, commonly used for circular, radial, or symmetrical forms.
Profile: The curve that will be rotated to form the surface.
Origin: The point where the rotation axis starts.
Direction (Input Vector): Defines the direction of the axis the profile spins around.
Angle: How far the profile rotates (e.g., 360° for a full shape).
Constructs a surface by interpreting a grid or structured list of points as a UV mesh.
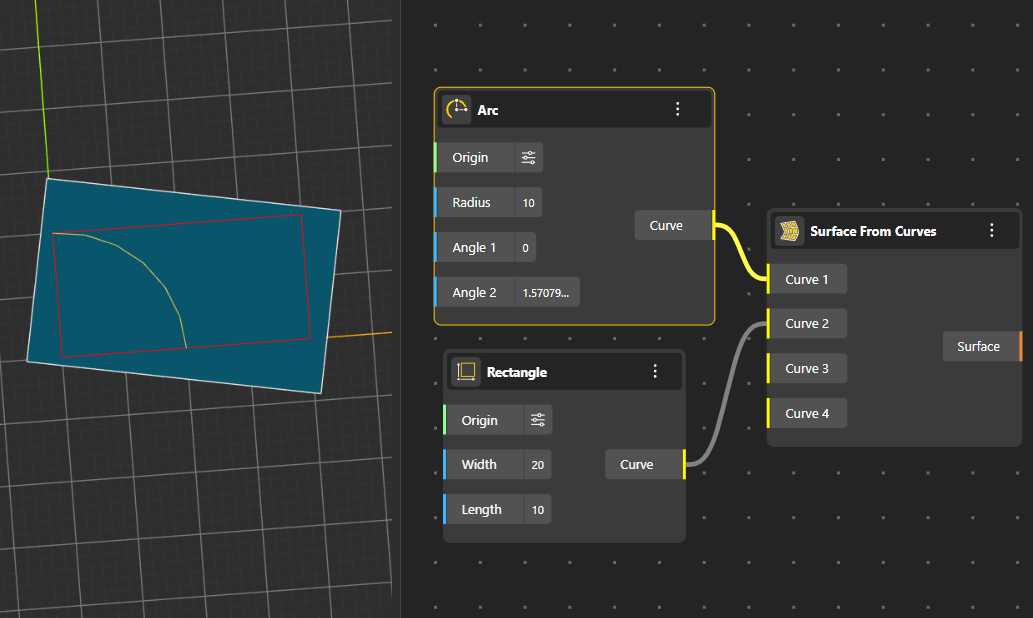
Creates a boundary-based surface using multiple input curves to define its perimeter.
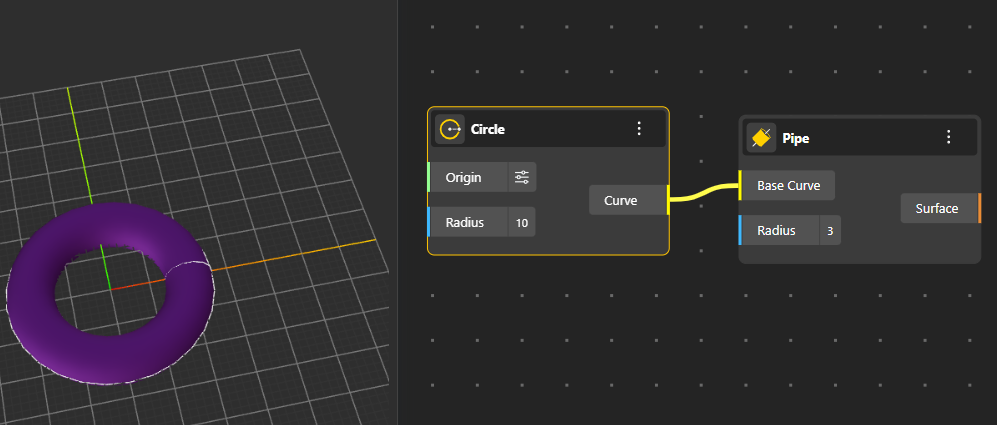
Produces a cylindrical or tubular surface for the input Radius, that follows the shape of a path curve.
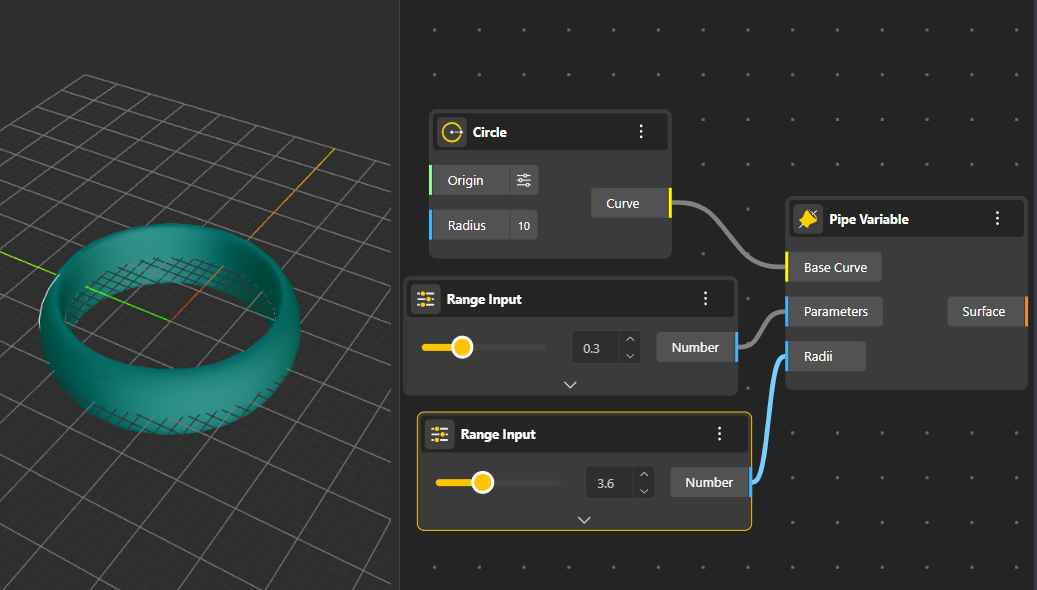
Creates a pipe whose radius changes along the curve, allowing tapered, bulged, or organically shaped tubes.
Base Curve: The path the pipe will follow.
Parameters: Positions along the curve (0 to 1) where the radius changes.
Radii: The radius values at those positions, controlling how thick or thin the pipe becomes.
Generates a surface defined by exactly four corner points, forming a flexible quadrilateral surface.
Builds a surface by selecting boundary edges, creating a surface that closely matches the surrounding geometry. Does not include the intersectional surface.
Combines two curves into one smooth, continuous surface. The first curve acts like the main path, and the second curve shapes how the surface transitions as it follows that path.
Creates a flat, rectangular surface based on width, height, or corner points.
Forms a circular planar surface defined by a radius or boundary circle.
Calculates the total area of a given surface.
Returns properties such as the point location, normal vector, or curvature at specific UV coordinates on the surface.
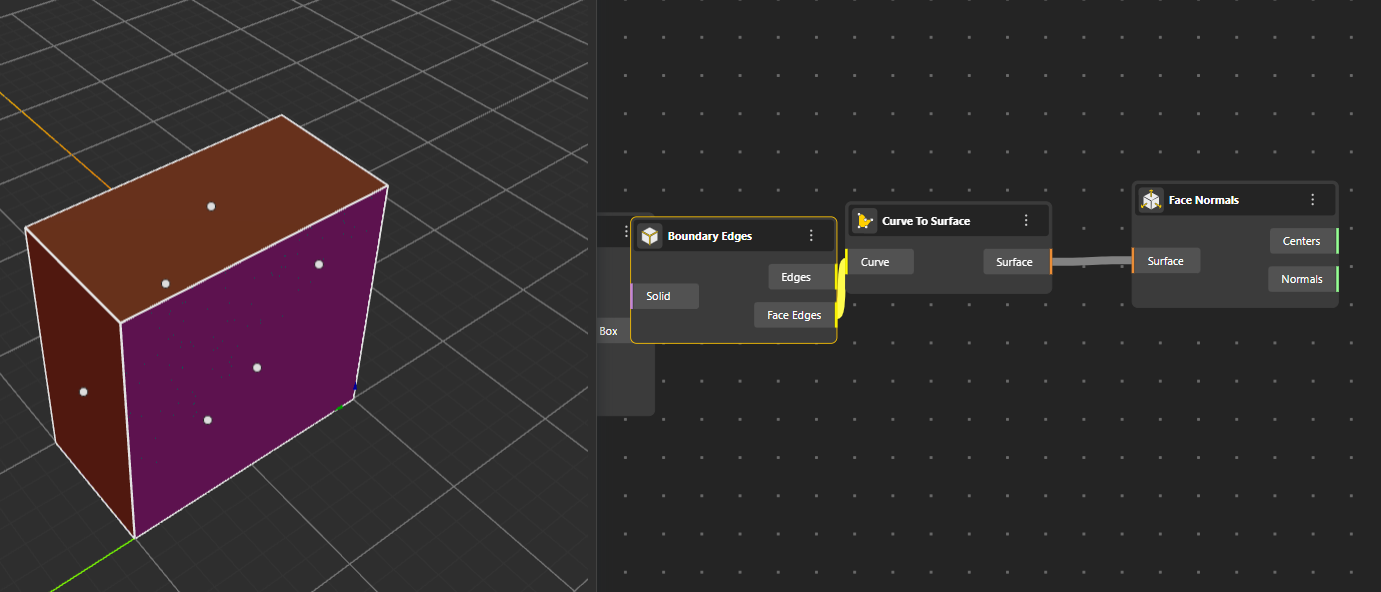
Extracts the boundary edges of a surface, separating them into individual curves. Output Port:
Edges: These are the outer boundary curves of the surface, the perimeter or outline that forms the visible border of the surface.
Face Edges: These are the inner edges created by trims, holes, or cut-outs on the surface, anything inside the boundary that also forms an edge.
Displays or retrieves the isocurves running along a surface’s U or V directions.
Computes the Normal and Center of each surface face, helpful for understanding orientation.
Closes open surfaces by generating flat or fitting end caps.
Creates a surface that is parallel and at a constant distance from the original one. Hide the Original Geometry Node for better preview.
Arc | Smooth, rounded transition | Parallel curve with arcs | Rounded surface extension |
Intersection | Stops/adjusts at intersections | Curve meets other geometry | Surface edges align with other surfaces |
Tangent | Preserves tangency, smoothness | Curve follows tangent direction | Surface offset preserves tangency |
Adds thickness along the sides of a surface, producing solid-like geometry from sheet-like forms.
Splits a surface into smaller panels or a UV grid, preparing it for patterning, tiling, or modular design. You can choose the U count and V count of Grid.